186x Filetype PDF File size 0.06 MB Source: www.cse.unsw.edu.au
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 1
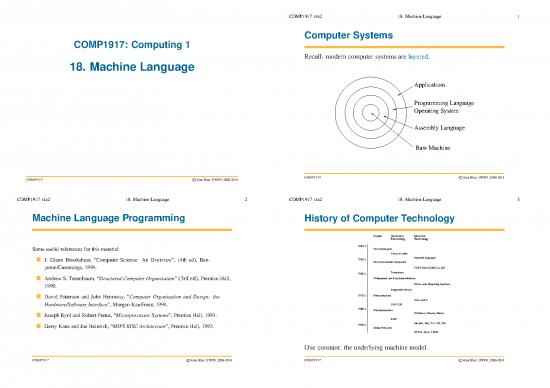
COMP1917: Computing1 ComputerSystems
18. Machine Language Recall: modern computer systems are layered.
Applications
Programming Language
Operating System
Assembly Language
Raw Machine
c
c COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 2 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 3
MachineLanguageProgramming History of Computer Technology
Impact Hardware Software
Technology Technology
1940’s
Someusefulreferences for this material: First prototypes
Vacuum tubes
J. Glenn Brookshear, “Computer Science: An Overview”, (4th ed), Ben- 1950’s Machine language
First commercial computers
jamin/Cummings, 1994. FORTRAN,COBOL,LISP
1960’s Transistors
AndrewS.Tanenbaum,“StructuredComputer Organisation” (3rd ed), Prentice-Hall, Widespread use in business/defence
1990. Multi−user Operating Systems
Integrated circuits
David Patterson and John Hennessy, “Computer Organization and Design: the 1970’s Minicomputers
Unix and C
Hardware/Software Interface”, Morgan-Kauffman, 1994. LSI/VLSI
1980’s Microprocessors
JosephByrdandRobertPettus,“MicroprocessorSystems”, Prentice Hall, 1993. Windows, Mouse, Menus
RISC
GerryKaneandJoeHeinrich,“MIPSRISCArchitecture”, Prentice Hall, 1992. 1990’s Haskell, Perl, Tcl, VB, OO
Global Network
HTML, Java, VRML
Oneconstant: the underlying machine model.
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 4 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 5
ComputerArchitecture Input/Output Devices
Vast range of devices are interfaced:
Device Read/Write Speed Notes
disks r/w high high-volume storage
Input
tape r/w low high-volume archiving
Processor Memory cd-rom r/o medium storage
Output display w/o medium CRT,LC,...
keyboard r/o low
mouse r/o low 1,3-button
• Processor: control, calculation other computers r/w varying networks
• Memory: data & program storage VR-helmet r/w high games
• Input/output: interface to the world mechanical r/w low embedded
equipment systems
c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 6 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 7
Central Processing Unit Processor (CPU)
Theprocessor’s task:
Processor {
Registers Register PC; /* program counter */
Arith/ M
Control Logic e forever {
Unit m
Unit o fetch instruction from Memory[PC++];
... r
y determine what kind of instruction;
fetch any necessary data;
carry out the specified operation;
}
}
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 8 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 9
Processor Operations FromHigh-level to Low-level Languages
CPUstypically provide operations for: Real machines can’t execute C directly.
• data movement (reg-to-reg, reg-to-mem) Real machines execute their own machine code.
C program source
• arithmetic calculation (e.g. + - * /) hello.c
• logical calculation (e.g. && || !) Compile gcc −S Complex task
• comparison (e.g. ==, >, <, >=, <=) hello.s Assembly code
• bit manipulation (e.g. ~ & | ^ >> <<) Assemble gcc −c
• program control (goto/branch) hello.o Machine code Simple task
Libraries Link gcc −o ...
• input/output (read, write) −l ...
hello
Machine code
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 10 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 11
Simulated Machine Architecture MachineLanguageSimulator
Main Memory
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Wewillbeusingasimulator called mlsim, similar to the one described in 1 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
“Computer Science: An Overview” by J. Glenn Brookshear. 2 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
3 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
256memorycells, with addresses from 00 to FF (hexadecimal) each 4 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
5 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
holding 1 byte (8 bits) 6 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
7 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
16 general-purpose registers (named R0 to RF) each holding 1 byte 8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
9 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
(8 bits) A 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
B 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
also a 1-byte program counter (PC) and a 2-byte instruction register C 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
D 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
(IR). E 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
F 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
R0:00 R1:00 R2:00 R3:00 R4:00 R5:00 R6:00 R7:00 PC:00
R8:00 R9:00 RA:00 RB:00 RC:00 RD:00 RE:00 RF:00 IR:0000
Type one of the following (H for help): M, R, P, C, S, G, F, Q:
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 12 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 13
Simulator-Program Commands: MachineLanguageInstructions
Options are as follows:
each machine instruction is 2 bytes (16 bits) long
M Change contents of memory cells. the first 4 bits comprise the op-code
R Change contents of registers.
P Change contents of program counter. the remaining 12 bits make up the arguments or “operands”
C Clear memory or registers. (Options will be given.)
S Single step. (Execute a single machine cycle.)
G Go. (Execute until a halt instruction is executed
or until 500 machine cycles have been executed.)
F List file options (to save or retrieve programs).
H Display this help screen.
Q Terminate this simulation program.
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 14 COMP191714s2 18. Machine Language 15
MachineLanguageInstructions MachineLanguageExamples
Op Args Description 14A3 store contents of the memory cell at address A3 into register R4.
1 RXY LOADregister R with contents of memory cell whose address is XY. 20A3 store the value A3 into register R0.
2 RXY LOADregister R with the bit pattern XY. 35B1 store the contents of register R5 into memory cell at address B1.
3 RXY STOREthecontents of register R in the memory cell with address XY. 40A4 copy the contents of register RA (R10) into register R4.
4 0RS COPYthebit pattern found in register R to register S. 5726 add binary values in registers R2 & R6 and store the sum in register R7.
5 RST ADDthebitpatterns in registers S & T as though they are 634E add the bit values in registers R4 and RE (R14) as floating-point numbers
2’s complement integers, and store the result in register R. and store the result in register R3.
6 RST ADDthebitpatterns in registers S & T as though they are 7CB4 ORthecontents of RB (R11) & R4 and store the result in register RC (R12).
floating point numbers, and store the floating point result in register R. 8045 ANDthecontents of registers R4 and R5 and store the result in register R0.
7 RST ORthebit patterns in registers S & T and store result in register R.
8 RST ANDthebitpatterns in registers S & T and store result in register R. 95F3 XORthecontents of RF (R15) & R3 and store the result in register R5.
9 RST XORthebitpatterns in registers S & T and store in register R. A403 rotate the contents of register R4 3 bits to the right in a circular fashion.
A R0X ROTATEthebit pattern in register R one bit to the right X times. B43C compare the contents of register R4 with the contents of register R0;
B RXY BRANCHtotheinstruction located in the memory cell at the address XY if the two are equal, pass control to the instruction at memory address 3C;
if the bit pattern in register R is equal to the bit pattern in register 0; otherwise, continue execution in its normal sequence.
otherwise, continue with the normal sequence of execution.
C 000 HALTexecution. C000 halt execution.
c c
COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014 COMP1917
AlanBlair,UNSW,2006-2014
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.