178x Filetype PDF File size 0.74 MB Source: mingycomputersgh.files.wordpress.com
PRIMARY 4
SECTION 1
ORAL SKILLS
General Objectives: The pupil will:
1. express himself or herself fluently .
2. develop their creative potentials.
3. appreciate the socio-cultural life of his or her community.
4. cultivate good morals, etiquette and co-operative skills.
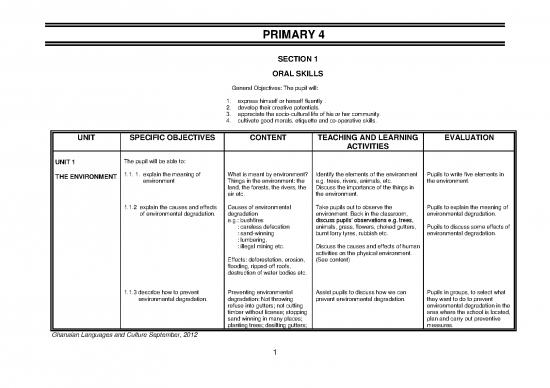
UNIT SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES CONTENT TEACHING AND LEARNING EVALUATION
ACTIVITIES
UNIT 1 The pupil will be able to:
THE ENVIRONMENT 1.1. 1. explain the meaning of What is meant by environment? Identify the elements of the environment Pupils to write five elements in
environment Things in the environment: the e.g. trees, rivers, animals, etc. the environment.
land, the forests, the rivers, the Discuss the importance of the things in
air etc. the environment.
1.1.2 explain the causes and effects Causes of environmental Take pupils out to observe the Pupils to explain the meaning of
of environmental degradation. degradation environment. Back in the classroom, environmental degradation.
e.g.: bushfires discuss pupils‟ observations e.g. trees,
: careless defecation animals, grass, flowers, choked gutters, Pupils to discuss some effects of
: sand-winning burnt lorry tyres, rubbish etc. environmental degradation.
: lumbering,
: illegal mining etc. Discuss the causes and effects of human
activities on the physical environment.
Effects: deforestation, erosion, (See content)
flooding, ripped-off roofs,
destruction of water bodies etc.
1.1.3 describe how to prevent Preventing environmental Assist pupils to discuss how we can Pupils in groups, to select what
environmental degradation. degradation: Not throwing prevent environmental degradation. they want to do to prevent
refuse into gutters; not cutting environmental degradation in the
timber without license; stopping area where the school is located,
sand winning in many places; plan and carry out preventive
planting trees; desilting gutters; measures.
Ghanaian Languages and Culture September, 2012
1
UNIT SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES CONTENT TEACHING AND LEARNING EVALUATION
ACTIVITIES
UNIT 2 The pupil will be able to:
TRADITIONAL 1.2.1 mention types of traditional Types of traditional sports and Discuss various traditional sports and Pupils play some traditional
SPORTS AND sports and games. games e. g. stone games, games that pupils play in their games.
GAMES oware, ampe, hide and seek, communities (See content)
draughts, tumatu etc. Note: Ensure that pupils wash their Mention some rules of the game.
hands with soap after the activity
1.2.2 describe a game and explain How a game is played and the Discuss how various games are played
how it is played rules governing it. and the specific rules governing them
1.2.3 identify the values of traditional Values: Help pupils to explain the meaning of Pupils discuss the values of
sports and games. - determination to win determination, teamwork and the others games.
- planning in the content.
- teamwork
- perseverance Pupils to select two sports or games and
- tolerance guide them to discuss the values in
- punctuality them.
- discipline etc.
UNIT 3
THE HOME 1.3.1 use the right register to Bedroom, hall, door, window, Use appropriately labelled pictures to Pupils draw a house and label its
describe their homes and roof, ceiling, wall, floor, teach the parts of a home and the items parts.
the items them. verandas, bathroom, toilet, at home
gate, kitchen, store room etc.
1.3.2 describe types of homes Types of homes: With the help of pictures, pupils to Pupils write at least four
available in their community. Mud, huts, wooden, describe different types of homes. sentences to describe their
Cement buildings. homes.
1.3.3 explain the importance of some Bedroom, windows, doors etc. Assist pupils to discuss the importance
parts of the home. (See content of 1.3.1) of the bedroom, hall, toilet and the others
in content.
1.3.4 explain why the kitchen must There is a lot of gases in Use the material in the content to
have two windows. kitchens that use firewood for introduce the lesson.
cooking. Some of these gases
are dangerous. There must Pupils to explain the meaning of
therefore be two windows, dangerous gases and explain why the
opposite each other in the kitchen must have two windows.
kitchen so that the bad air will
flow out easily.
Ghanaian Languages and Culture September, 2012
2
UNIT SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES CONTENT TEACHING AND LEARNING EVALUATION
ACTIVITIES
UNIT 3 (CONT’D) The pupil will be able to:
THE HOME 1.3.5 explain why the toilet must be Germs like dirty and smelly Guide pupils to explain why the toilet Pupils use disinfectant to clean
kept clean all the time. places. The toilet must must be kept clean all the time. the school urinal.
therefore be kept clean all the
time to help us to avoid Pupils to describe some of the things we
sickness from germs. must use to keep the toilet clean.
Cleaning items: broom,
scrubbing brush and soap;
disinfectant like Dettol, Izal etc.
UNIT 4
GIVING DIRECTIONS
USING LANDMARKS 1.4.1 explain the meaning of Landmarks are important Use a simple map of the locality to
landmarks with examples. buildings, objects or places in a discuss the meaning of landmarks.
community that can be seen
and identified easily. Pupils to give examples of landmarks in
Eg. their community, town or village.
- Post office
- Bridges
- Hills
- Curves
- Trees
1.4.2 use various landmarks in the Pupils use landmarks to answer the
area to give directions. following questions: Pupils give directions to their
homes and other places in the
i. Where is your home located? community using landmarks to
Ii Where does your teacher live? the class for the class to ask
iii. In which direction is the market? etc questions.
Ghanaian Languages and Culture September, 2012
3
UNIT SPECIFIC CONTENT TEACHING AND LEARNING EVALUATION
OBJECTIVES ACTIVITIES
The pupil will be able to:
UNIT 5
1.5.1 tell the time by hours, by Using the clock to tell time in hours, Guide pupils to tell the time using the clock Pupils use the clock face to
TELLING THE TIME half past and quarter past half past and quarter past or quarter face. tell the time you call out.
or quarter to the hour. to. eg.
It is 2 o‟clock (Use hours, half past,
There are sixty minutes in the hour. It is 30 minutes past 2 o‟clock; It is half past quarter past and quarter etc)
15 minutes of the 60 minutes makes 2 o‟clock .
a quarter of the hour. 15 minutes to It is quarter to four etc.
the hour is therefore a quarter to the
hour; and 15 minutes past the hour, Stress the following:
is quarter past the hour. - the right-hand movement of the
hand of the clock.
- Terms for telling the time:
o‟clock, quarter past,
quarter to……...
1.5.2 tell the time by hours and
minutes. Minutes after……. Using the clock face, pupils to explain the
Minutes to…….. number of minutes in an hour.
Help pupils to understand the differences
between am and pm in telling time.
Pupils individually describe the position of the
hour and minutes hands for the following
times:
3.25 am
9.40 pm
NOTE: You may have to teach this lesson
again to make sure every pupil has
understood the lesson.
1.5.3 tell the names and
sequence of days of the Calendar months and weeks. Using a calendar, assist pupils to learn the Pupils write names of the
week and the months months of the year and the days of the week. days of the week and
of the year. 30 days have September, April, NOTE: Use a poem or song (if available) to months of the year.
June and November. All the rest teach this lesson. You may also compose
have 31, except February alone one.
. which has 28 days and 29 days in a Pupils to answer questions on the following
leap year. and more:
On which day do we go to church?
When is Easter celebrated?
When is Id-Ul-Fitr observed?
In which month is Odwira/Damba celebrated
Ghanaian Languages and Culture September, 2012
4
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.