165x Filetype PDF File size 2.84 MB Source: www.facs.org
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS DIVISION OF EDUCATION
Groin Hernia Repair
Inguinal and Femoral
The Condition Many patients become symptomatic after
Patient Education the fi rst 1 to 2 years and crossover to surgery
A hernia occurs when tissue bulges out due to increased pain on exertion, chronic
This educational information is to through an opening in the muscles. constipation or urinary symptoms.3
help you be better informed about Any part of the abdominal wall can
your operation and empower you weaken and develop a hernia, but
with the skills and knowledge the most common sites are the groin Benefits and Risks
needed to actively participate in (inguinal), the navel (umbilical) and of Your Operation
your care. a previous surgical incision site.
Common Symptoms B e n e fi t s — An operation is the only way
Keeping You to repair a hernia. You can return to
●Visible bulge in the scrotum or groin your normal activities and in most cases
Informed area, especially with coughing will not have further discomfort.
Information that will help you or straining Possible risks include—Return of the
further understand the operation ●Pain or pressure at the hernia site hernia; infection; injury to the bladder,
and your role in your recovery. blood vessels, intestines or nerves,
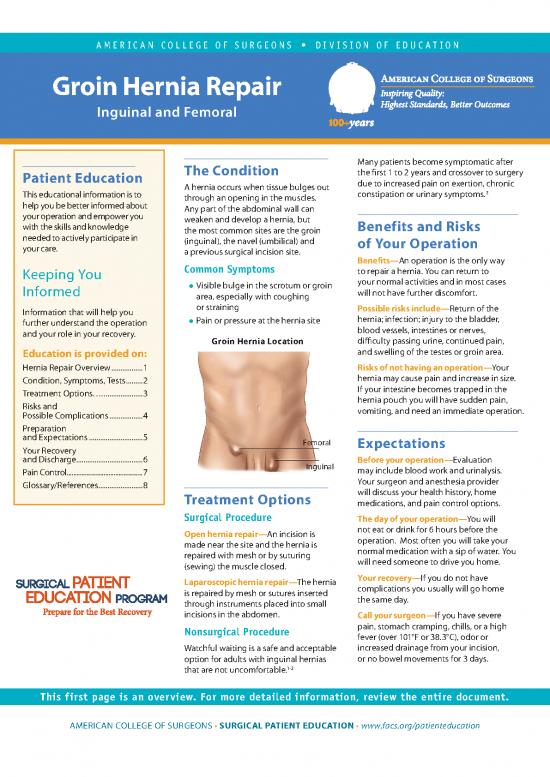
Groin Hernia Location diffi culty passing urine, continued pain,
Education is provided on: and swelling of the testes or groin area.
Hernia Repair Overview .................1 Risks of not having an operation—Your
Condition, Symptoms, Tests .........2 hernia may cause pain and increase in size.
Treatment Options….. ....................3 If your intestine becomes trapped in the
Risks and hernia pouch you will have sudden pain,
Possible Complications ..................4 vomiting, and need an immediate operation.
Preparation
and Expectations .............................5 Femoral Expectations
Your Recovery
and Discharge ....................................6 Inguinal Before your operation—Evaluation
Pain Control.............................................7 may include blood work and urinalysis.
Glossary/References ........................8 Your surgeon and anesthesia provider
Treatment Options will discuss your health history, home
medications, and pain control options.
Surgical Procedure The day of your operation—You will
Open hernia repair—An incision is not eat or drink for 6 hours before the
made near the site and the hernia is operation. Most often you will take your
repaired with mesh or by suturing normal medication with a sip of water. You
(sewing) the muscle closed. will need someone to drive you home.
Laparoscopic hernia repair—The hernia Your recovery—If you do not have
is repaired by mesh or sutures inserted complications you usually will go home
through instruments placed into small the same day.
incisions in the abdomen. Call your surgeon—If you have severe
Nonsurgical Procedure pain, stomach cramping, chills, or a high
fever (over 101°F or 38.3°C), odor or
Watchful waiting is a safe and acceptable increased drainage from your incision,
option for adults with inguinal hernias or no bowel movements for 3 days.
1-2
that are not uncomfortable.
This first page is an overview. For more detailed information, review the entire document.
AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS SURGICAL PATIENT EDUCATION www.facs.org/patienteducation
Groin Hernia Repair
The Condition, Symptoms, Inguinal and Femoral
and Diagnostic Tests SAMPLE
Keeping You
Informed Inguinal canal
Groin Hernia Fat
Who Gets Hernias? Muscle
There may be no cause
for a hernia. Some risk
factors are:
Older age—muscles Hernia with intestine
become weaker
Obesity—increased Spermatic cord
weight places
pressure on
abdominal muscle
Sudden twist,
pulls, or strains
Chronic straining Femoral Symptoms
Family history
Connective tissue Inguinal The most common symptoms are:
disorders ● Bulge in the groin, scrotum, or
Pregnancy—1 in abdominal area that often increases
2,000 women in size with coughing or straining.
develop a hernia The Condition ● Mild pain or pressure at the hernia site.2
during pregnancy.2 The Hernia ● Numbness or irritation due to pressure
Other medical on the nerves around the hernia.2
A groin hernia occurs when the intestine ● Sharp abdominal pain and vomiting
disorders bulges through the opening in the muscle
that have symptoms in the groin area. A reducible hernia can be can mean that the intestine has slipped
similar to hernias include pushed back into the opening. When intestine through the hernia sac and is strangulated.
enlarged lymph nodes, or abdominal tissue fills the hernia sac and This is a surgical emergency and
cysts, and testicular cannot be pushed back, it is called irreducible immediate treatment is needed.
problems such as or incarcerated. A hernia is strangulated if
scrotal hydrocele.2-4 the intestine is trapped in the hernia pouch
and the blood supply to the intestine is Common Tests
decreased. This is a surgical emergency.2
2
History and Physical exam
There are two types of groin hernias:
An inguinal hernia appears as a bulge in the The site is checked for a bulge.
groin or scrotum. Inguinal hernias account for Other tests may include (see glossary):
75% of all hernias and are most common in men.2 ● Digital exam
A femoral hernia appears as a bulge in the groin, ● Blood tests
upper thigh, or labia (skin folds surrounding ● Urinalysis
the vaginal opening). Femoral hernias are ten ● Electrocardiogram (ECG)—for patients
2
times more common in women. They are always over 45 or if high risk of heart problems
1-3
repaired because of a high risk of strangulation. ● Ultrasound
Herniorraphy is the surgical repair of a hernia. ● Computerized tomography (CT) scan
Hernioplasty is the surgical repair of a hernia
with mesh.
2 AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS SURGICAL PATIENT EDUCATION www.facs.org/patienteducation
Groin Hernia Repair
Surgical and Inguinal and Femoral
Nonsurgical Treatment
Open Repair Laparoscopic Repair
Muscle
Inguinal ring Inguinal ring
Mesh plug Spermatic cord
Open Mesh Mesh Port
Nerve and genital
branch of nerve
Surgical Treatment Suture Only
The type of operation depends on hernia size Muscle
and location, and if it is a repeat hernia. Your Inguinal ring Port sites will vary
health, age, anesthesia risk, and the surgeon’s Spermatic cord
expertise are also important. An operation Sutured muscle
is the only treatment for incarcerated/ Nerve and genital
strangulated and femoral hernias. branch of nerve Mesh repair
Your hernia can be repaired either as
an open or laparoscopic approach.
The repair can be done by using sutures Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
only or adding a piece of mesh.
Open Hernia Repair The surgeon will make several small punctures
or incisions in the abdomen. Ports (hollow
The surgeon makes an incision near tubes) are inserted into the openings. The
the hernia site and the bulging tissue abdomen is inflated with carbon dioxide gas Keeping You
is pushed back into the abdomen. to make it easier to see the internal organs. Informed
Most inguinal hernia repairs use mesh Surgical tools and a laparoscopic light are
5 placed into the ports. The hernia is repaired with
to close the muscle. An open repair Open vs. Laparoscopic
can be done with local anesthesia. mesh and sutured or stapled in place. The repair Incisional Repair
● For an open mesh repair: The hernia sac is done as a TransAbdominal PrePeritoneal
is removed. Mesh is placed over the hernia (TAPP) procedure, which means the peritoneum A laparoscopic repair of inguinal
site. The mesh is attached using sutures (the sac that contains all of the abdominal hernia may result in less pain
sewn into the stronger tissue surrounding organs) is entered, or the repair is done as a and numbness, lower infection
Totally ExtraPeritoneal (TEP) procedure.2-4 rate, and faster return to normal
the hernia site. Mesh plugs can also be activity when compared with open
placed into the inguinal or femoral hernia 6
space. The mesh plug fills the open site Nonsurgical Treatment surgery. Laparoscopic repair may
and is sutured to the surrounding tissue. lengthen the operative time and
5
An additional mesh patch is applied Watchful waiting is an option if you have may cost more. A recurrence from
2 1 a previous open hernia repair is
and may or may not be sutured. Mesh an inguinal hernia with no symptoms. best repaired laparoscopically
is often used for large hernia repairs Hernia incarceration occurred in 1.8 per because you avoid scar tissue from
and may reduce the risk that the hernia 1,000 men who waited longer than 2 years
2 7
will come back. The site is closed using to have a repair. Femoral hernias should previous incisions. Laparoscopic
sutures, staples, or surgical glue. always be repaired because of the high risk repair of a bilateral (both sides
● For a suture-only repair: The hernia (400 of 1,000) of incarceration and bowel of the groin) inguinal hernias
sac is removed. Then the tissue along strangulation within 2 years of diagnosis.2 also resulted in earlier return
8
the muscle edge is sewn together. Trusses or belts can help manage the symptoms to work than open repairs.
This procedure is often used for of a hernia by applying pressure at the site. A The risk of complications
strangulated or infected hernias or truss requires correct fitting and increases for both the open and
small defects (less than 3 cm). complications include testicular nerve laparoscopic procedure if the
4 9
damage and incarceration may result. hernia extends into the scrotum.
3
Groin Hernia Repair
Risks of this Procedure Inguinal and Femoral
SAMPLE
Risks Based on the ACS Risk Calculator
Open and Laparoscopic Inguinal and Femoral Hernia Surgery from the ACS Risk Calculator—July 17, 2018
Risks Percent for Keeping You Informed
Average Patient
Wound Infection: Infection at the Open 0.3% Antibiotics and drainage of the wound may be needed.
area of the incision or near the organ Laparoscopic 0.2% Smoking can increase the risk of infection.
where the surgery was performed
Complications: Including surgical Open 1.5% Complications related to general anesthesia and surgery may be higher
infections, breathing difficulties, Laparoscopic 1.2% in smokers, elderly and/or obese patients, and those with high blood
blood clots, renal (kidney) pressure and breathing problems. Wound healing may also be decreased
complications, cardiac complications, in smokers and those with diabetes and immune system disorders.
and return to the operating room
Pneumonia: Infection in the lungs Open 0.1% Movement, deep breathing, and stopping smoking
Laparoscopic 0.1% can help prevent respiratory infections.
Urinary tract infection: Infection Open 0.1% Drinking fluids and catheter care decrease the risk of bladder infection.
of the bladder or kidneys Laparoscopic 0.1%
Venous thrombosis: A blood clot in Open 0.1% Longer surgery and bed rest increase the risk. Getting up, walking 5
the legs that can travel to the lungs Laparoscopic 0.1% to 6 times per day, and wearing support stockings reduce the risk.
Death Less than 1% Your surgical team is prepared for all emergency situations.
Risks from Outcomes Reported Percent for Keeping You Informed
in the Last 10 years of Literature Average Patient
Chronic (long-term) pain 10% to 12% may have Factors contributing to chronic pain include emergency hernia repair,
1
pain one year after scrotal hernia, or recurrent hernia repair. Pain may be less with laparoscopic
2
surgery; possibly less procedures than open procedures. Pain caused by compression or tension
10-12 13
with lapraoscopic may gradually decrease with time as a result of tissue rearrangement.
14
Recurrence: A hernia can All patients 1% to 17% Recurrence occurs half as often when mesh is used versus non-
2
recur after the repair Open 4.9% mesh repair. Laparoscopic repair is recommended for recurrent
Laparoscopic 10.1% hernias because the surgeon avoids previous scar tissue. There is a
higher rate of recurrence in older men with laparoscopic repair.
Neuralgia: Nerve pain causing Open 10.7% Pressure, staples, stitches, or a trapped nerve in the surgical area
tingling or numbness Laparoscopic 7.4% can cause nerve pain. Tell your doctor if you feel severe, sharp, or
tingling pain in the groin and leg immediately after your procedure;
an operation may be required if the nerve is trapped.2
Seroma: A collection of Mesh repairs 8% Seromas can form around the former hernia site. Removal
clear/yellow fluid Nonmesh repairs 3.1% of fluid with a sterile needle may be required.2-4
Hematoma: a collection of blood Mesh repairs 2.2% Hematomas are treated with anti-inflammatory medications,
in the wound site or scrotum Nonmesh repairs 7% elevation, and rest. Rarely blood replacement or further
testing for a blood vessel injury is needed.4
The data have been averaged per 1,000 cases
The ACS Surgical Risk Calculator estimates the risk of an unfavorable outcome. Data is from a large number of patients
who had a surgical procedure similar to this one. If you are healthy with no health problems, your risks may be below
average. If you smoke, are obese, or have other health conditions, then your risk may be higher. This information is not
intended to replace the advice of a doctor or health care provider. To check your risks, go to the ACS Risk Calculator at
http://riskcalculator.facs.org.
4 AMERICAN COLLEGE OF SURGEONS SURGICAL PATIENT EDUCATION www.facs.org/patienteducation
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.