338x Filetype PPTX File size 0.38 MB Source: uomustansiriyah.edu.iq
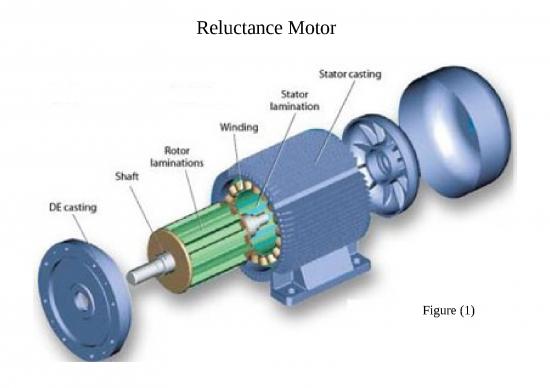
Reluctance Motor
The origin of this motor can be traced back to 1842. The
Synchronous reluctance motor has a stator wounded as that
of a 3-phase induction machine. It works as a synchronous
motor without DC field winding in its rotor.
A reluctance motor is a type of electric motor that induces
non-permanent magnetic poles on the ferromagnetic rotor.
Torque is generated through the phenomenon of magnetic
reluctance. Hence, it is not a permanent magnet motor,
because its salient rotor is composed of soft ferromagnetic
material (of a thin hysteresis loop with high remanence and
small coercive force).
Construction of Reluctance Motor Rotor
1- Notch-Type Rotor
• “Notch” areas are of
“High-Reluctance”
• “Pole” areas are known as
“Salient” Poles
• Number of salient poles
must match the number
of stator poles
Figure (2)
2- Flat and Barrier Slot Rotors
Figure (4)
Principle of Operation
When a piece of magnetic
material is free to move in a
magnetic field, it will align
itself with the magnetic field
to minimize the reluctance of
the magnetic circuit. To put it
another way the piece will
orient itself towards the
magnetic pole creating the
field. The torque on the rotor
created in this way is called
the reluctance torque. Figure (5)
• Rotor accelerates towards synchronous
speed
• At a “critical” speed, the low-
reluctance paths provided by the salient
poles will cause them to “snap” into
synchronism with the rotating flux.
• When the rotor synchronizes, slip is
equal to zero
• Rotor pulled around by “reluctance
torque”
• Figure (6) shows the rotor
Figure (6)
synchronized at no load.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.