256x Filetype PPTX File size 0.43 MB Source: issr.edu.kh
10 Questions
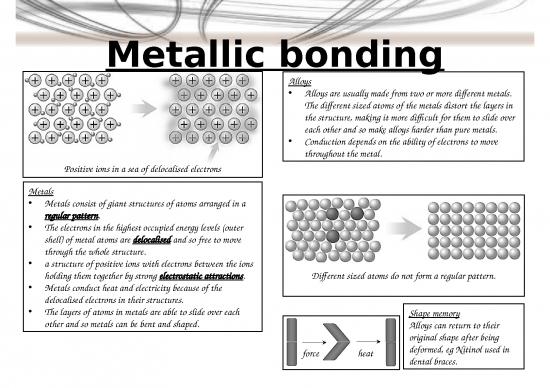
1. What type of bonding do metals have?
2. Draw a diagram to show the arrangement of atoms in a metal.
3. Do metals have a regular or irregular structure?
4. What is the main purpose of alloying metals?
5. What are alloys called that can return to their original shape?
6. How can we return them to their original shape?
7. What happens to valence (outer) electrons in a metal?
8. What forces of attraction hold metal atoms together?
9. Why can metals conduct electricity?
10. Draw a diagram to show the bonding present in solid sodium.
Metallic bonding
Mark Scheme
Metallic bonding Polymers and Nanoscience
1. Metallic 1. High Density (HD)
2. 2. Thermosoftening
3. Thermosetting
4. Cross-links in the structure
5. The melting point of a thermosoftening polymer is
determined by the strength of the INTERMOLECULAR
3. Regular FORCES
4. To make them harder 6. Gets bigger
5. Shape memory alloys 7. Nanoscience is the science of very small particles and looks
6. Heat them up at the properties of nanoparticles.
7. The outer electrons of metal atoms are delocalised and so 8. A nanoparticle is about 100 atoms
free to move through the whole structure. 9. Advantages:
8. Strong electrostatic attractions. • Large surface area makes them effective catalysts.
9. Metals conduct heat and electricity because of the • Nanotubes can be used in small scale circuits as
delocalised electrons. nanowires.
10. Disadvantages:
• So small they can enter the skin and therefore the
bloodstream.
• Easily become airborne, breathing in can potentially
damage the lungs.
10. Sun screens (or) Bandages - others
Positive ions in a sea of delocalised electrons
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.