| POTENTIAL FAILURE MODE AND EFFECTS ANALYSIS (DESIGN FMEA) |
|
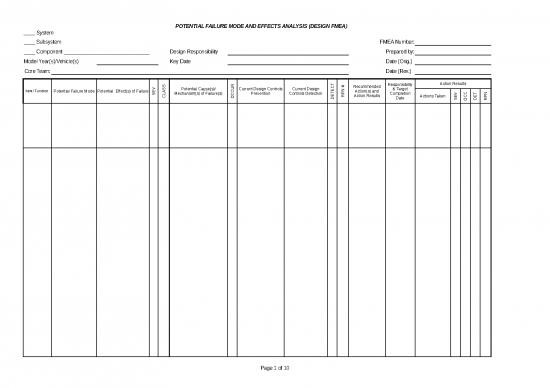
Type of DFMEA - System is a high level combination of various subsystems and components. Examples of systems are chassis system, powertrain system, interior system, etc.
____ System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subsystem is a subset of a larger system. Examples are front suspension being a subset of the chassis system, or wheel assembly being a subset of the chassis system.
____ Subsystem |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tracking Number. How do we track it?
FMEA Number: |
|
|
|
Component is a sub-set of a subsystem. An example would be a shock absorber is a component of the front suspension which is a subsystem of the chassis system.
____ Component ____________________ |
|
___________________ |
|
|
Who has responsibility for the design? OEM, your company, supplier, a combination?
Design Responsibility |
|
|
Person's name, phone number and company that is responsible for the DFMEA
Prepared by: |
|
|
|
If known, the vehicle program and model years affected by this product
Model Year(s)/Vehicle(s) |
|
|
|
The date the initial DFMEA is due, which is before the scheduled production design release date.
Key Date |
|
|
Date the original DFMEA was completed
Date (Orig.) |
|
|
|
Each team member's name and department
Core Team: |
|
|
The latest revision date. When was it last updated?
Date (Rev.) |
|
|
|
What functions are supposed to be performed by the product?
What is it we are analyzing (feature , characteristic)? What is it supposed to do? regulatory requirements?
Item/ Function |
What is the negative or opposite of the function? How can it fail to meet or deliver the intended function?
Potential Failure Mode |
What are the effects to the customers if the failure occurs.
Typical effects are: noise, rough, erratic, inoperative, unpleasant, poor appearance, unstable, intermittent, leaks, operation impaired, regulatory non-compliance.
Potential Effect(s) of Failure |
What is the level of severity if the failure occurs? Use the table in the worksheet attached.
SEV |
Identify any key or significant characteristics and government regulations. Use customer symbols when required. Identify key characteristics whether self identified or customer identified.
CLASS |
List all the underlying potential root causes of the failure to the left. May often be more than one. Give each potential cause their own cell or box
Potential Cause(s)/ Mechanism(s) of Failure(s) |
Likelihood or probability of the failure occurring. Use the table in the attached worksheet
OCCUR |
What is being done to minimize the Occurrence or prevent the failure from occurring?
Current Design Controls Prevention |
What is being done to detect the potential failure? What checks, inspections, tests, etc?
Current Design Controls Detection |
The likelihood or probability that the potential failure will be detected and caught. Use the table in the attached worksheet.
DETECT |
Risk Priority Number that is S x O x D.
Severity x Occurrence x Detection.
RPN # |
If the risk is too high what do we plan to do to lower the risk? Also records the results of actions taken.
Recommended Action(s) and Action Results |
Who is responsible for taking the action and by when?
This is a high liability concern if action is not taken or is not timely.
Responsibility & Target Completion Date |
Action Results |
|
What was actually done and accomplished? This may differ from the Recommended Actions.
Actions Taken |
Severity ranking after the action was taken. May be different from what was originally planned and anticipated.
SEV |
Occurrence ranking after the action was taken. May be different from what was originally planned and anticipated.
OCC |
Detection ranking after the action was taken. May be different from what was originally planned and anticipated.
DET |
New RPN after the action was taken. May be different from what was originally planned and anticipated.
RPN |
List the function of the item being analyzed to meet the design intent.
|
Typical failure modes: cracked, deformed, loose, leaking, sticking, oxidized, fractured, slips, inadequate, intermittent, no signal, drift, etc.
Describe in physical or technical terms, not as a symptom necessarily noticeable by the customer
|
All levels of customers should be considered.
Next operation,
Downstream ops,
Outsources,
Subcontractors,
Assembly plants,
Vehicle owners,
Vehicle drivers,
Gov't regulations.
|
|
A key characteristic is a product characteristic or manufacturing process parameter which can affect safety or compliance with government regulations, fit, function, performance, or subsequent processing of the product.
|
|
|
Any Poke-Yokes, mistake proofing, fail-safes?
These process controls justify the OCCURRENCE score and have no affect on Detection scores.
Examples include material certs, specs, checklists, standardized work, preventive maintenance, 5S, tool change notifications, gage calibrations and GR&R, etc.
|
List all process controls that help detect and prevent the potential failure, including subsequent, downstream controls. All the combined controls justify the detection score. These include controls that detect the failures or causes after they occur.
|
The score is based on all detections at this process step and downstream that are listed to the left. Subsequent process controls downstream may help reduce the detection score, but must be referenced to the left at this process step.
The detection values must be selected to reflect the robutsness or ability of the detection technique to discover and control the cause of the failure mode or the actual failure itself.
|
Some customers and companies dictate a threshold score that demands subsequent action (i.e. RPN > 100 requires action because there is an unacceptable level of risk). Best practice is for companies to evaluate all their PFMEAs and paretoize the top scores, then creat action items for the top 2 to 5 every year, in addition to addressing high RPN's above the acceptable threshold or level of risk. Other best practices evaluate S * O >35 for significant potential sources of customer concerns should detection devices fail.
|
Best practice is to show proposed actions and anticipated RPN change based on the action to be taken (i.e. 7 x 5 x 5). A good record of the plan and risk reduction.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| SUGGESTED DESIGN FMEA SEVERITY RANKINGS |
|
|
|
|
|
| Severity Effect |
Criteria: Severity of Effect on Product (Customer Effect) |
Ranking |
| Failure to Meet Safety and/or Regulatory Requirements |
Potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation without warning |
10 |
| Potential failure mode affects safe vehicle operation and/or involves noncompliance with government regulation with warning |
9 |
| Loss or Degradation of Primary Function |
Loss of primary function (Vehicle inoperable, does not affect safe vehicle operation). |
8 |
| Degradation of primary function (vehicle operable, but at reduced level of performance). |
7 |
| Loss or Degradation of Secondary Function |
Loss of secondary function (vehicle operable, but comfort/convenience functions inoperable). |
6 |
| Degradation of secondary function (vehicle operable, but comfort/convenience functions at reduced level of performance). |
5 |
| Annoyance |
Appearance or Audible Noise, vehicle operable, item does not conform and noticed by most customers (>75%). |
4 |
| Appearance or Audible Noise, vehicle operable, item does not conform and noticed by many customers (50%) |
3 |
| Appearance or Audible Noise, vehicle operable, item does not conform and noticed by discriminating customers (<25%). |
2 |
| No effect |
No discernible effect. |
1 |
| SUGGESTED DESIGN FMEA OCCURRENCE RANKINGS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Probability of Failure |
Likely Failure Rates |
Likely Failure Rates |
Ppk |
Ranking |
| Very High: Persistent Failures |
> 100 per thousand pieces 100,000 ppm or 10% |
More than one occurrence per day |
<0.55 |
10 |
| 50 per thousand pieces 50,000 ppm or 5% |
One occurrence every 3 to 4 days |
>0.55 |
9 |
| High: Frequent Failures |
20 per thousand pieces 20,000 ppm or 2% |
One occurrence per week |
>0.78 |
8 |
| 10 per thousand pieces 10,000 ppm or 1% |
One occurrence every month |
>0.86 |
7 |
| Moderate: Occasional Failures |
5 per thousand pieces 5,000 ppm or 0.5% |
One occurrence every three months |
>0.94 |
6 |
| 2 per thousand pieces 2,000 ppm or 0.2% |
One occurrence every six months |
>1.00 |
5 |
| 1 per thousand pieces 1,000 ppm or 0.1% |
One occurrence per year |
>1.10 |
4 |
| Low: Relatively Few Failures |
1 in 2,000 pieces 500 ppm or 0.05% |
One occurrence every 1 to 3 years |
>1.20 |
3 |
| 1 in 10,000 pieces 100 ppm or 0.01% |
One occurrence every 3 to 5 years |
>1.30 |
2 |
| Remote: Failure is Unlikely |
1 in 100,000 pieces 10 ppm or 0.001% |
One occurrence greater than 5 years |
>1.67 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
| Note: Likely failure rates are based on internal occurences only, not frequency of defect escapes to |
|
|
|
|
| the customer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Note: Same table as PFMEA |
|
|
|
|