183x Filetype PDF File size 0.16 MB Source: www.stmarysdubai.com
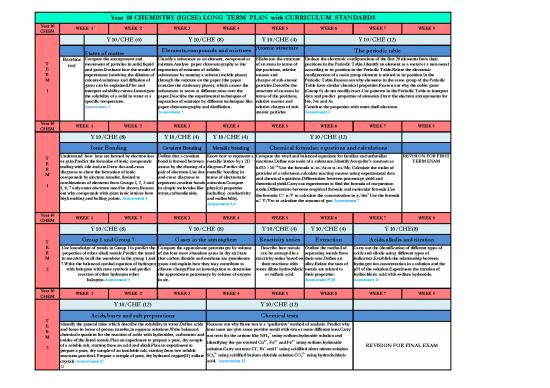
Year 10 CHEMISTRY (IGCSE) LONG TERM PLAN with CURRICULUM STANDARDS
Year 10 WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 WEEK 6 WEEK 7 WEEK 8
CHEM
Y 10/CHE (6) Y 10/CHE (8) Y 10/CHE (4) Y 10/CHE (12)
States of matter Elements,compounds and mixtures Atomic structure The periodic table
Baseline Compare the arrangement and Classify a substance as an element, compound or Ellaborate the structure Deduce the electronic configurations of the first 20 elements from their
T test movement of particles in solid,liquid mixture.Analyse paper chromatography as the of an atom in terms of positions in the Periodic Table.Identify an element as a metal or a non-metal
E and gases.Evaluate how the results of separation of mixtures of soluble the positions, relative according to its position in the Periodic Table.Relate the electronic
R experiments involving the dilution of substances by running a solvent (mobile phase) masses and configuration of a main group element is related to its position in the
M coloured solutions and diffusion of through the mixture on the paper (the paper charges of sub-atomic Periodic Table.Reason out why elements in the same group of the Periodic
gases can be explained.Plot and contains the stationary phase), which causes the particles.Describe the Table have similar chemical properties.Reason out why the noble gases
1 interpret solubility curves.Investigate substances to move at different rates over the structure of an atom in (Group 0) do not readily react.Use patterns in the Periodic Table to interpret
the solubility of a solid in water at a paper.Describe the experimental techniques of terms of the positions, data and predict properties of elements.Draw the electron arrangements for
specific temperature. separation of mixtures by different techniques like relative masses and He, Ne and Ar.
Assessment 1 paper chromatography and distillation. relative charges of sub- Correlate the properties with outer shell electrons.
Assessment 2 atomic particles Assessment 3
Year 10 WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 WEEK 6 WEEK 7 WEEK 8
CHEM
Y 10/CHE (8) Y 10/CHE (4) Y 10/CHE (4) Y 10/CHE (12)
Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Metallic bonding Chemical formulae, equations and calculations
T Understand how ions are formed by electron loss Define that a covalent Know how to represent a Compare the word and balanced equations for familiar and unfamiliar REVISION FOR FIRST
E or gain.Predict the formulae of ionic compounds bond is formed between metallic lattice by a 2D reactions.Define one mole of a substance.Identify Avogadro's constant as TERM EXAM
ending with -ide and ate.Draw dot-and-cross atoms by the sharing of a diagram.Predict the 23.
R diagrams to show the formation of ionic pair of electrons.Use dot- metallic bonding in 6.023 × 10 Use the formula n=m/Ar or n=m/Mr. Calculate the moles of
M compounds by electron transfer, limited to and-cross diagrams to terms of electrostatic particles of a substance.calculate reacting masses using experimental data
combinations of elements from Groups 1, 2, 3 and represent covalent bonds attraction.Compare and chemical equations.Differentiate between percentage yield and
1 5, 6, 7 only outer electrons need be shown.Reason in simple molecules like physical properties theoretical yield.Carry out experiments to find the formula of magnesium
out why compounds with giant ionic lattices have water,carbondioxide. including conductivity oxide.Differentiate between empirical formula and molecular formula.Use
the formula C= n/V to calculate the concentration in g/dm3.Use the formula
high melting and boiling points. Assessment 4 and malleability.
Assessment 5,6 n= V/Vm to calculate the amount of gas. Assessment 7
Year 10 WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 WEEK 6 WEEK 7 WEEK 8
CHEM
Y 10/CHE (8) Y 10/CHE (8) Y 10/CHE (4) Y 10/CHE (4) Y 10/CHE(8)
T Group 1 and Group 7 Gases in the atmosphere Reactivity series Extraction Acids,alkalis and titration
E Use knowledge of trends in Group 1 to predict the Compare the approximate percentages by volume Describe how metals Outline the method of Carry out the identification of different types of
R properties of other alkali metals.Predict the trend of the four most abundant gases in dry air.State can be arranged in a separating metals from acids and alkalis using different types of
M in reactivity in all the members in the group 1 and that carbon dioxide and methane are greenhouse reactivity series based on their ores.Define an indicators.Establish the relationship between
7.Write the balanced symbol equation of hydrogen gases and explain how they may contribute to their reactions with alloy.Relate the uses of hydrogen ion concentration in a solution and the
2 with halogens with state symbols and predict climate changePlan an investigation to determine water dilute hydrochloric metals are related to pH of the solution.Experiment the titration of
reaction of other hydrogen other the approximate percentage by volume of oxygen or sulfuric acid. their properties. hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide.
halogens.Assessment 8 in air. Assessment 9,10 Asessment 11
Year 10 WEEK 1 WEEK 2 WEEK 3 WEEK 4 WEEK 5 WEEK 6 WEEK 7 WEEK 8
CHEM
Y 10/CHE (12) Y 10/CHE (12)
Acids,bases and salt preparations Chemical tests
T Identify the general rules which describe the solubility in water.Define acids Reasons out why flame test is a ‘qualitative’ method of analysis. Predict why
E and bases in terms of proton transfer,in aqueous solutions.Write balanced ions must not give same positive result with two or more different ions.Carry
R chemical equations for the reaction of acids with hydroxides, carbonates and +
M oxides of the listed metals.Plan an experiment to prepare a pure, dry sample out tests for the cations like NH4 using sodium hydroxide solution and
2+ 2+ 3+
of a soluble salt, starting from an acid and alkali.Plan an experiment to identifying the gas evolved Cu , Fe and Fe using sodium hydroxide REVISION FOR FINAL EXAM
2 prepare a pure, dry sample of an insoluble salt, starting from two soluble solution.Carry out tests Cl–, Br– and I– using acidified silver nitrate solution
reactants.practical. Prepare a sample of pure, dry hydrated copper(II) sulfate SO 2– using acidified barium chloride solution CO 2– using hydrochchloric
4 3
crystals. Assessment 12 acid. Assessment 13
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.