180x Filetype PDF File size 0.44 MB Source: www.stfrancisschool.edu.in
Class- X
Chemistry
Chapter-5
Periodic Classification of Elements
‘’The periodic table is a tabular method of displaying the elements in such a
way, that the elements having similar properties occur in the same vertical
column or group”.
Without the classification of elements, it would be extremely difficult and
time-consuming to individually study the chemistry of all the elements. Hence,
to simplify and systematize the study of elements and their compounds, they
are classified into groups and periods.
Early Models of Periodic Table
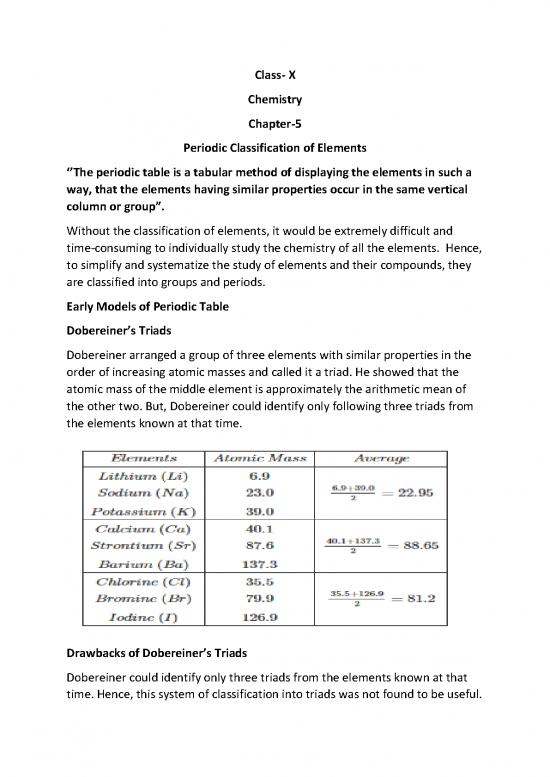
Dobereiner’s Triads
Dobereiner arranged a group of three elements with similar properties in the
order of increasing atomic masses and called it a triad. He showed that the
atomic mass of the middle element is approximately the arithmetic mean of
the other two. But, Dobereiner could identify only following three triads from
the elements known at that time.
Drawbacks of Dobereiner’s Triads
Dobereiner could identify only three triads from the elements known at that
time. Hence, this system of classification into triads was not found to be useful.
Newlands’ Law of Octaves
According to this ‘when elements are placed in order of increasing atomic
masses, the physical and chemical properties of every 8th element are a
repetition of the properties of the first element.’
Newlands compared these octaves to the series of eight notes of a musical
scale.
sa (do) re (re) ga (mi) ma (fa) pa (so) da (la) ni (ti)
H Li Be B C N O
F Na Mg Al Si P F
Cl K Ca Cr Ti Mn Fe
Co and Cu Zn Y In As Se
Ni
Br Rb Sr Ce and La Zr ______ _____
Limitations of Newlands’ Law of Octaves
• Law of octaves was applicable only up to calcium (only for lighter
elements). As after calcium every eighth element did not possess
properties similar to that of the first.
• Newland adjusted two elements in the same slot (e.g., Co and Ni),
having different properties. For example; Co and Ni with Fluorine,
Chlorine, Bromine and Iodine.
• In order to fit elements into his Table, Newlands adjusted two elements
in the same slot, but also put some unlike elements under the same
note. For example, cobalt and nickel are in the same slot and these are
placed in the same column as fluorine, chlorine and bromine which have
very different properties than these elements. Iron, which resembles
cobalt and nickel in properties, has been placed far away from these
elements.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Table:
Mendeleev’s periodic table is based on the physical and chemical properties of
elements and their atomic masses.
Mendeleev’s Periodic Law
According to this “The physical and chemical properties of the elements are
the periodic function of their atomic masses.”
Periodicity of Properties:
The repetition of properties of elements after certain regular intervals is
known as Periodicity of Properties.
Features of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
● Six horizontal rows, known as periods.
● Eight vertical columns known as groups.
● Groups I to VII subdivided into A and B subgroups.
● Groups VIII doesn’t have any subgroups and contains three elements in each
row.
● Elements in the same group exhibit similar properties.
Achievements of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table
A systematic study of elements:
Elements with similar properties were grouped together, that made the study
of their chemical and physical properties easier.
Correction of atomic masses:
Placement of elements in Mendeleev’s periodic table helped in correcting the
atomic masses of certain elements. For example, the atomic mass of beryllium
was corrected from 13.5 to 9. Similarly, atomic masses of indium, gold,
platinum etc., were also corrected.
Prediction of properties of yet to be discovered elements:
Mendeleev’s left vacant places in his table which provided an idea for the
discovery of new elements. Example: Eka-boron, Eka-aluminium and Eka-
silicon.
Mendeleev’s periodic table was predicted properties of several
undiscovered elements on the basis of their position in Mendeleev’s periodic
table.
These elements, when discovered were named scandium, gallium, and
germanium respectively.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.