227x Filetype PDF File size 0.18 MB Source: chui-science.weebly.com
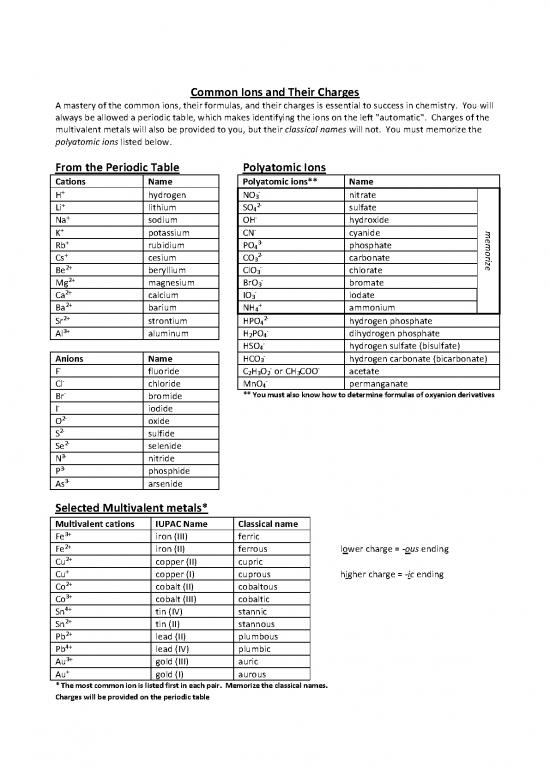
Common Ions and Their Charges
A mastery of the common ions, their formulas, and their charges is essential to success in chemistry. You will
always be allowed a periodic table, which makes identifying the ions on the left "automatic". Charges of the
multivalent metals will also be provided to you, but their classical names will not. You must memorize the
polyatomic ions listed below.
From the Periodic Table Polyatomic Ions
Cations Name Polyatomic ions** Name
+ ‐
H hydrogen NO nitrate
3
+ 2‐
Li lithium SO sulfate
4
+ ‐
Na sodium OH hydroxide
+ ‐ memorize
K potassium CN cyanide
+ 3‐
Rb rubidium PO phosphate
4
+ 2‐
Cs cesium CO carbonate
3
2+ ‐
Be beryllium ClO chlorate
3
Mg2+ magnesium BrO‐ bromate
3
2+ ‐
Ca calcium IO iodate
3
2+ +
Ba barium NH ammonium
4
Sr2+ strontium HPO2‐ hydrogen phosphate
4
3+ ‐
Al aluminum HPO dihydrogen phosphate
2 4
‐
HSO hydrogen sulfate (bisulfate)
4
Anions Name HCO ‐ hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate)
3
‐ ‐ ‐
F fluoride CHO or CHCOO acetate
2 3 2 3
‐ ‐
Cl chloride MnO permanganate
4
‐ ** You must also know how to determine formulas of oxyanion derivatives
Br bromide
‐
I iodide
2‐
O oxide
2‐
S sulfide
Se2‐ selenide
3‐
N nitride
P3‐ phosphide
As3‐ arsenide
Selected Multivalent metals*
Multivalent cations IUPAC Name Classical name
Fe3+ iron (III) ferric
Fe2+ iron (II) ferrous lower charge = ‐ous ending
2+
Cu copper (II) cupric
+
Cu copper (I) cuprous higher charge = ‐ic ending
Co2+ cobalt (II) cobaltous
Co3+ cobalt (III) cobaltic
Sn4+ tin (IV) stannic
Sn2+ tin (II) stannous
2+
Pb lead (II) plumbous
4+
Pb lead (IV) plumbic
3+
Au gold (III) auric
+
Au gold (I) aurous
* The most common ion is listed first in each pair. Memorize the classical names.
Charges will be provided on the periodic table
Tips for Learning the Ions
Monatomic Ions
1. For many ions, their location on the table suggests their charge:
a. All Group 1 elements (alkali metals) lose one electron to form a 1+ ion.
b. All Group 2 elements (alkaline earth metals) lose two electrons to form a 2+ ion.
c. Group 13 metals like aluminum lose three electrons to form a 3+ ion.
d. All group 17 elements (halogens) gain one electron to form a 1‐ ion.
e. All group 16 non‐metals gain two electrons to form a 2‐ ion.
f. All group 15 non‐metals gain three electrons to form a 3‐ ion.
2. Metals that can form more than one ion will have their positive charge denoted by a Roman numeral
in parentheses immediately next to the name of the cation.
Polyatomic Ions: Oxyanion Derivatives
Alot of learning the polyatomic ions just boils down to memorization, but there are a number
of patterns.
1. The "‐ate" anions have one more oxygen than the "‐ite" ion, but the same charge.
+
2. Some polyatomic ions are derived by bonding another polyatomic ion to hydrogen (H ). Since
hydrogen has a charge of 1+, the resulting anion will have a charge that is less negative by one.
example: PO 3‐ ‐‐‐‐> HPO 2‐ ‐‐‐‐> H PO ‐
4 4 2 4
phosphate hydrogen phosphate dihydrogen phosphate
3. Learn the hypochlorite ‐‐> chlorite ‐‐> chlorate ‐‐> perchlorate series, which applies to the other
halogen oxyanions (iodate and bromate) as well.
a. The relationship between "ite" and "ate" is predictable, as always.
b. The prefix "hypo" means "under" or "too little" (think "hypodermic" or "hypothermic").
c. The prefix
"hyper" means "above" or "too much" (think "hyperactive").
d. Notice that the charge always remains the same.
‐ ‐ ‐ ‐
example: ClO ‐‐‐‐> ClO ‐‐‐‐> ClO ‐‐‐‐> ClO
2 3 4
hypochlorite chlorite chlorate perchlorate
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.