181x Filetype PDF File size 0.17 MB Source: chemrevise.files.wordpress.com
Revision Guide: 4.1 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
Atoms,ElementsandCompounds
Atoms
Compounds
All substances are made of atoms. An atom is the
Some elements combine through chemical
smallest part of an element that can exist.
reactions to form compounds.
Atoms of each element are represented by a chemical
Compounds are made from two or more
symbol,egOrepresents an atom of oxygen, Na
different elements (types of atoms) combined
represents an atom of sodium.
together in fixed proportions and can be
represented by formulae using the symbols of
Elements and the periodic Table
the atoms from which they were formed, e.g CO
2
Anelement is a substance with only one type of atom.
Elements are listed in the periodic table. There are about 100
Compoundshavedifferent propertiesfrom the
different elements.
elements they are made from.
Elements can be classified as metal or non-metal depending
Compounds canonly be separated into elements
on their properties.
by chemical reactions.
The columns in the periodic table are called groups and
contain similar elements.
The rows in the periodic table are called periods. Elements
show a gradual change in properties across a period
Mixtures
Separating Techniques
A mixture consists of two or more elements or compounds not Mixtures can be separated by physical processes
chemically combined together. such as filtration, crystallisation, simple distillation,
The chemical properties of each substance in the mixture are fractional distillation and chromatography. These
unchanged. physical processes do not involve chemical
reactions.
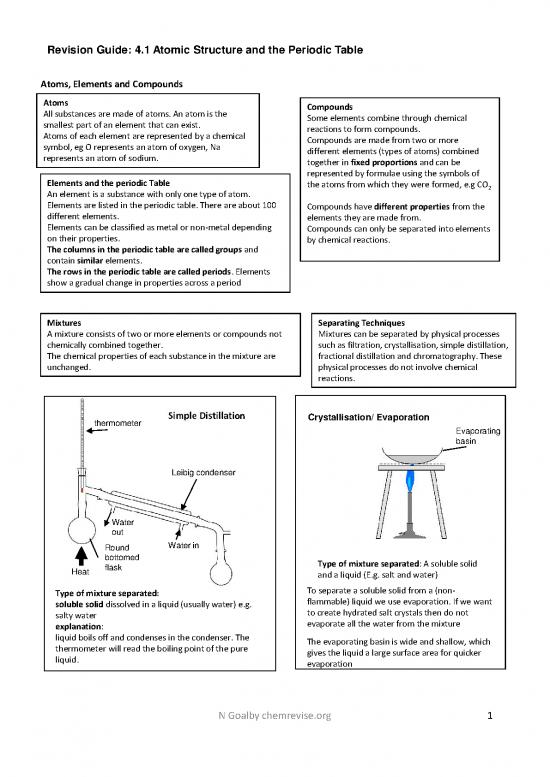
thermometer Simple Distillation Crystallisation/ Evaporation
Evaporating
basin
Leibig condenser
Water
out
Round Water in
bottomed
Heat flask Type of mixture separated: A soluble solid
and aliquid(E.g. salt and water)
To separate a soluble solid from a (non-
Typeof mixture separated:
flammable) liquid we use evaporation. If we want
soluble solid dissolved in a liquid (usually water) e.g.
to create hydrated salt crystals then do not
salty water
evaporate all the water from the mixture
explanation:
liquid boils off and condenses in the condenser. The
The evaporating basin is wide and shallow, which
thermometer will read the boiling point of the pure
gives the liquid a large surface area for quicker
liquid.
evaporation
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1
Fractional Distillation
Filtration
Fractionating
column Liebig condenser
Filter
residue paper
Filter
funnel
filtrate
Type of mixture separated:
insoluble solid suspended in a liquid
Type of mixture separated:
(usually water) e.g. sand and water.
Soluble liquids with different boiling points e.g. crude oil
Explanation:
The fractionating column has a temperature gradient and
Theinsoluble solid (called residue) gets caught in
is hotter at the bottom than at the top
the filter paper, because the particles are too big
to fit through the holes in the paper.
Explanation: When a mixture of soluble liquids is heated all
The filtrate is the substance that comes through
liquids are evaporated. The liquid with the lower boiling point,
the filter paper.
however, forms the greatest percentage of vapour. As the
vapourmoves up the fractionating column it becomes more
rich with the component that has the lowest boiling point. This
is due to the vapour mixture condensing and evaporating as it
movesup thecolumn.
A thermometer measures thetemperature of the fractions
before they condense. The liquid with the lowest boiling point
will be the first 'fraction' to collect.
Seechapter 4.8for information about chromatography
2
NGoalbychemrevise.org
History of Development of the Atom
Before the discovery of the electron atoms were thought to be tiny spheres that could not be divided
Plum-puddingmodel
Thediscovery of the electron led to
the plum-pudding model of the
electrons
atom. The plum-pudding model
suggested that the atom was a ball
of positive charge with negative
electrons embedded in it
Nuclearmodel
The results from the Rutherford and Marsden’s alpha scattering experiments
led to the plum-pudding model being replaced by the nuclear model.
electrons
This experiment showed that all the mass of the atom was in the centre.
This was called the nucleus.
nucleus
The electrons were thought to orbit the nucleus, like planets around the sun.
Nuclear model
In the experiment most of the alpha particles directed at thin gold foil
passed through but a few bounced back, suggesting the positive charge
was concentrated at the centre of each gold atom.
x
Bohr Model xx
Neils Bohr adapted the nuclear model by suggesting that electrons orbit the x
nucleus at specific distances.
x x electrons
x x
The electrons are on energy levels or shells x
The theoretical calculations of Bohr agreed with experimental observations
x x nucleus
Bohr Model
Later experiments led to the idea that the positive charge of any nucleus could be subdivided into a whole
number of smaller particles, each particle having the same amount of positive charge. The name proton was
given to these particles
Chadwick
Theexperimental work of James Chadwick provided the evidence to show the existence of neutronswithin the
nucleus. This was about 20 years after the nucleus became an accepted scientific idea. This could help explain
the existence of isotopes
N Goalby chemrevise.org 3
The Atom
Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge
Atoms have a small central nucleus made
Proton 1 +1
up of protons and neutrons around which
Neutron 1 0
there are electrons.
Electron Very small -1
In an atom, the number of electrons is
Size of atom
equal to the number of protons in the
Atomsare very small, having a radius of about
-10
nucleus. Atoms have no overall electrical
0.1 nm (1x 10 m).
charge.
The radius of a nucleus is less than 1/10 000 of
-14
that of the atom (about 1 x 10 m).
All atoms of a particular element have the
same number of protons.
The number of protons in an atom is called its atomic number
Atomsof different elements have different
(proton number). Atoms are arranged in the modern periodic
numbers of protons.
table in order of their atomic number (proton number).
To work out the number of neutrons in an atom subtract the
Most of the mass of an atom is in the nucleus
atomic number from the mass number
Example Beryllium : atomic number 4, mass number 9.
The total number of protons and neutrons in
It has 4 protons, 4 electrons
an atom is called its mass number
and9-4 =5 neutrons
An atom of Lithium (Li) can be represented as follows:
Mass Number 7 Li Atomic Symbol
Atomic Number 3
Theatomic number,is the number of protons in the nucleus.
Themass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom.
Number of neutrons = A - Z
Isotopes
Atomsof the same element can have different numbers of neutrons; these atoms are called isotopes of that element.
Isotopes of an element have the same chemical properties because they have the same electronic structure
Calculating Relative Atomic Mass
Therelative atomic mass of an element is an average value that takes account of
the abundance of the isotopes of the element.
35 37
R.A.M = (isotopic mass x % abundance) Example 1. Chlorine has two isotopes Cl and Cl. 75% of a
35 37
100 sample of chlorine is Cl and 25% is Cl.
Calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine
R.A.M = [(75 x 35) + (25 x 37)] /100
= 35.5
N Goalby chemrevise.org 4
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.