177x Filetype PDF File size 0.49 MB Source: ajaybhadouriya.files.wordpress.com
CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
&
PERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS
BY- A.P.S. BHADOURIYA, M.Sc. , B.Ed., NET,
During the nineteenth century, chemists began to categorize the elements according to similarities in their physical
and chemical properties. The end result of these studies was our modern periodic table.
Lavoisier (1789) classified elements into metals, non-metals, gases and earths.
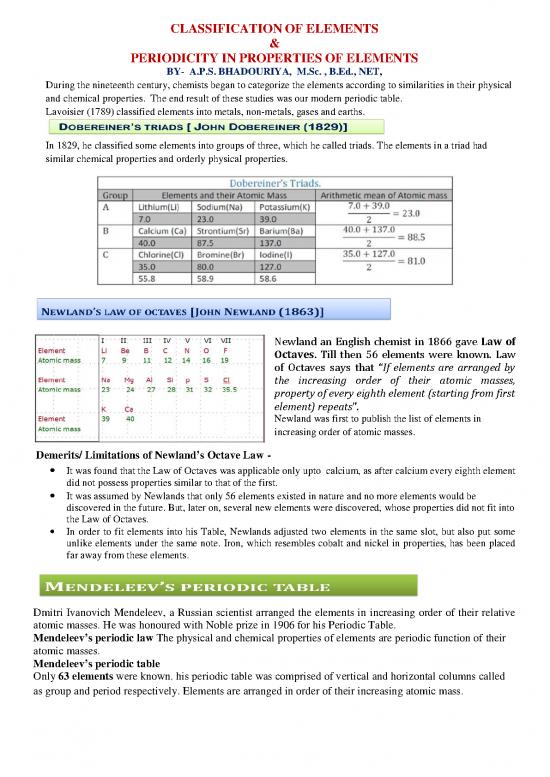
In 1829, he classified some elements into groups of three, which he called triads. The elements in a triad had
similar chemical properties and orderly physical properties.
Newland an English chemist in 1866 gave Law of
Octaves. Till then 56 elements were known. Law
of Octaves says that “If elements are arranged by
the increasing order of their atomic masses,
property of every eighth element (starting from first
element)repeats”.
Newland was first to publish the list of elements in
increasing order of atomic masses.
Demerits/ Limitations of Newlands Octave Law -
It was found that the Law of Octaves was applicable only upto calcium, as after calcium every eighth element
did not possess properties similar to that of the first.
It was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be
discovered in the future. But, later on, several new elements were discovered, whose properties did not fit into
the Law of Octaves.
In order to fit elements into his Table, Newlands adjusted two elements in the same slot, but also put some
unlike elements under the same note. Iron, which resembles cobalt and nickel in properties, has been placed
far away from these elements.
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, a Russian scientist arranged the elements in increasing order of their relative
atomic masses. He was honoured with Noble prize in 1906 for his Periodic Table.
Mendeleevs periodic law The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic function of their
atomic masses.
Mendeleevs periodic table
Only63 elements were known. his periodic table was comprised of vertical and horizontal columns called
as group and period respectively. Elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic mass.
GROUPS- 8 vertical rows.
7 groups were subdivided in A and B.
th
8 group has 9 elements in the group of 3 each.
PERIODS– 7 horizontal rows
Merits of Mendeleev's Periodic Table:-
Mendeleev left some blank spaces in his periodic table in order to place the elements having similar
properties in the same group.
For example; titanium has been placed in IVth group, leaving a blank space adjacent to it in IIIrd
group. Similarly, arsenic has been placed in Vth group; leaving two adjacent spaces blank. These
spaces have been occupied by scandium, gallium and germanium after their subsequent discovery.
Mendeleev predicted the discovery of some elements and named them as eka-boron, eka-aluminium
and eka-silicon. He gave the name of these elements prefixing the word 'eka' to the name of the
preceding elements. Scandium, Gallium and Germanium have been discovered later and took the
place of eka-carbon, ekaaluminium and eka-silicon, respectively in the gap left in the Mendeleev's
Periodic table; as their properties Were exactly similar to the predicted elements.
Position of Noble gases which were discovered later:-
Noble gases were discovered much later after Mendeleev. After the discovery of noble gas, they
were placed in a separate group called Zero Group, after VIII group, without making any disturbance
to the arrangement of any elements in the Mendeleev's Periodic Table. Noble gases are chemically
un-reactive and present in very low concentration in the atmosphere.
He corrected the atomic masses of Be, In, and U . He stated that if the atomic weight of an element
caused it to be placed in the wrong group, then the weight must be wrong.
Limitation of Mendeleev's Periodic Table
Position of Hydrogen:-
Hydrogen has been placed in 1st group with alkali metals, since hydrogen makes compound in the
same way as alkali metals do. On the other hand, hydrogen exists as diatomic molecule; similar to
halogen and hydrogen makes covalent compounds also as halogens do.
Position of Isotopes:-
Elements having same atomic number but different atomic masses are known as isotopes. Although
isotopes were discovered after Mendeleev, but it became a challenge to accommodate those isotopes
in Mendeleev's Periodic Table without disturbing the order of elements.
Wrong Order of Elements:-
Mendeleev placed many elements in wrong order of their increasing atomic masses in order to place
elements having similar properties in similar group.
Example: The atomic mass of nickel is less than that of cobalt; in spite of that cobalt is placed before
nickel. The atomic mass of Chromium is 50.20 and the atomic mass of vanadium is 50.94. In spite
of this, chromium is placed after vanadium.
In spite of above limitations and anomalies, the Mendeleev's Periodic Table was one of the
wonderful discoveries.
English physicist, Henry Moseley observed regularities in the characteristic X-ray spectra. A plot of f against atomic
number (Z ) of the elements gave a straight line and not the plot of f vs atomic mass
He thereby showed that the atomic number is a more fundamental property of an element than its atomic mass.
Mendeleevs Periodic Law was, therefore, accordingly modified. This is known as the Modern Periodic Law and can
be stated as :
The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers.
Cause of periodicity : Periodicity may be defined as the repetition of the similar properties of the elements
placed in a group and separated by certain definite gap of atomic numbers.
The cause of periodicity is the resemblance in properties of the elements is the repetition of the same
valence shell electronic configuration.
Features of Modern Periodic Table:-
Elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic numbers.
The vertical columns are known as groups and horizontal columns are known as periods; in the modern
periodic table.
There are 18 groups and 7 periods in the modern periodic table.
Elements having same number of valence electrons are placed in the same group. Elements in a group have
similar but not identical electronic configuration and properties .
Elements having same number of shells are placed in the same period. They contains 2,8,8,18,18,32 and 28
elements respectively
Position of Elements in the Modern Periodic Table –
a) Finding Period of Elements:
Period of the element is equal to highest energy level or shell of electrons or principal quantum number(n)
Look at following examples for better understanding
b) Finding Group of Elements:
Group of element in group A is equal to number of valence electrons of element or number of electrons in
the highest energy level of elements if this No. is 1 or 2. If No. of electrons is more than 2 than its group
will be 10 + number of electrons in the highest energy level.ie. if there are x electron in valence shell then
Group No =x if x ≤2 and
Group No =10+x if x is ≥ 3 and
Elements in group B have n and (n-1) shells incomplete, here total number of electrons in these shells -8
gives us group of element.
Look at following examples.
Q. Find the position of P (Z=15) ,Ca(Z=20) and Fe(Z=26) in periodic table
a) P =2,8,5
rd
Period= 3 , its highest energy level is 3
th
Group=10+ 5=15 (sinceelectron in its outer most shell are more than 2)
b) Ca =2,8,8,2
th
Period= 4 , its highest energy level is 4
nd
Group=2 ( since 2electron are there in its outer most shell)
a) Fe =2,8,14,2 (two outermost shells are incomplete)
th
Period= 4 , its highest energy level is 4
Group=(14+2)–8=8th
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.