248x Filetype PDF File size 0.34 MB Source: sixthresearcher.com
Python 3 Beginner's Reference Cheat Sheet Alvaro Sebastian
http://www.sixthresearcher.com
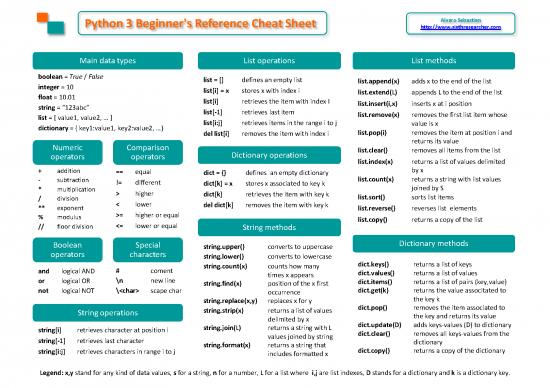
Main data types List operations List methods
boolean = True / False list = [] defines an empty list list.append(x) adds x to the end of the list
integer = 10 list[i] = x stores x with index i list.extend(L) appends L to the end of the list
float = 10.01 list[i] retrieves the item with index I list.insert(i,x) inserts x at i position
string = “123abc” list[-1] retrieves last item
list = [ value1, value2, … ] list.remove(x) removes the first list item whose
dictionary = { key1:value1, key2:value2, …} list[i:j] retrieves items in the range i to j value is x
del list[i] removes the item with index i list.pop(i) removes the item at position i and
Numeric Comparison returns its value
operators operators Dictionary operations list.clear() removes all items from the list
list.index(x) returns a list of values delimited
+ addition == equal dict = {} defines an empty dictionary by x
- subtraction != different dict[k] = x stores x associated to key k list.count(x) returns a string with list values
* multiplication > higher dict[k] retrieves the item with key k joined by S
/ division list.sort() sorts list items
** exponent < lower del dict[k] removes the item with key k list.reverse() reverses list elements
% modulus >= higher or equal list.copy() returns a copy of the list
// floor division <= lower or equal String methods
Boolean Special string.upper() converts to uppercase Dictionary methods
operators characters string.lower() converts to lowercase
and logical AND # coment string.count(x) counts how many dict.keys() returns a list of keys
times x appears dict.values() returns a list of values
or logical OR \n new line string.find(x) position of the x first dict.items() returns a list of pairs (key,value)
not logical NOT \ scape char occurrence dict.get(k) returns the value associtated to
string.replace(x,y) replaces x for y the key k
String operations string.strip(x) returns a list of values dict.pop() removes the item associated to
delimited by x the key and returns its value
string[i] retrieves character at position i string.join(L) returns a string with L dict.update(D) adds keys-values (D) to dictionary
values joined by string dict.clear() removes all keys-values from the
string[-1] retrieves last character string.format(x) returns a string that dictionary
string[i:j] retrieves characters in range i to j includes formatted x dict.copy() returns a copy of the dictionary
Legend: x,y stand for any kind of data values, s for a string, n for a number, L for a list where i,j are list indexes, D stands for a dictionary and k is a dictionary key.
Python 3 Beginner's Reference Cheat Sheet Alvaro Sebastian
http://www.sixthresearcher.com
Built-in functions Conditional Loops Functions
statements
print(x, sep='y') prints x objects separated by y if : while : def function():
input(s) prints s and waits for an input
that will be returned else if : return
for in :
len(x) returns the length of x (s, L or D) …
else: Modules
min(L) returns the minimum value in L for in
max(L) returns the maximum value in L range(start,stop,step): import module
sum(L) returns the sum of the values in L if in : module.function()
range(n1,n2,n) returns a sequence of numbers for key, value in from module import *
from n1 to n2 in steps of n Data validation dict.items(): function()
abs(n) returns the absolute value of n try: Reading and
round(n1,n) returns the n1 number rounded Loop control writing files
to n digits except : statements
f = open(,‘r')
type(x) returns the type of x (string, float, else: break finishes loop f.read()
list, dict …) execution f.readline()
str(x) converts x to string continue jumps to next f.close()
Working with files iteration
list(x) converts x to a list and folders pass does nothing f = open(,’r’)
int(x) converts x to a integer number for line in f:
import os Running external
float(x) converts x to a float number os.getcwd() programs f.close()
help(s) prints help about x os.makedirs() import os f = open(,'w')
os.chdir() f.write()
map(function, L) Applies function to values in L os.listdir() os.system() f.close()
Legend: x,y stand for any kind of data values, s for a string, n for a number, L for a list where i,j are list indexes, D stands for a dictionary and k is a dictionary key.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.