223x Filetype PDF File size 0.10 MB Source: resources.finalsite.net
Aquatic Environmental Science Scope & Sequence
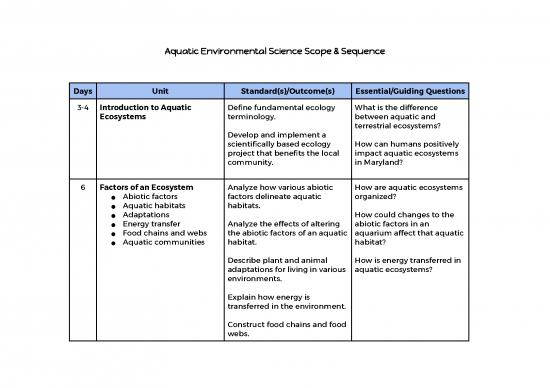
Days Unit Standard(s)/Outcome(s) Essential/Guiding Questions
3-4 Introduction to Aquatic Define fundamental ecology What is the difference
Ecosystems terminology. between aquatic and
terrestrial ecosystems?
Develop and implement a
scientifically based ecology How can humans positively
project that benefits the local impact aquatic ecosystems
community. in Maryland?
6 Factors of an Ecosystem Analyze how various abiotic How are aquatic ecosystems
● Abiotic factors factors delineate aquatic organized?
● Aquatic habitats habitats.
● Adaptations How could changes to the
● Energy transfer Analyze the effects of altering abiotic factors in an
● Food chains and webs the abiotic factors of an aquatic aquarium affect that aquatic
● Aquatic communities habitat. habitat?
Describe plant and animal How is energy transferred in
adaptations for living in various aquatic ecosystems?
environments.
Explain how energy is
transferred in the environment.
Construct food chains and food
webs.
Describe how abiotic factors
play a role in the aquatic biotic
community
6 Properties of Water Explain water’s ability to How do factors of water
● Temperature and basic support organisms. affect biotic and abiotic
properties factors in aquatic
● Chemicals dissolved in Explain how dissolved ecosystems?
water chemicals in water affect living
● Variation of water organisms. How does turbidity affect the
temperature process of photosynthesis?
● Turbidity Compare water temperatures
● Light transmission and from one body of water to
photosynthesis another, and within a single
● Water depth and related body of water.
factors
● Hydrologic cycle Explain the importance of light
● Watershed transmission to photosynthesis.
7 Groundwater Model the components of a How is water held in soil and
● Water table water table, including rock?
● Water in soil and rock saturated
● Wetlands and hydrology and unsaturated zones, How does groundwater
● Filtering pollution capillary impact aquatic ecosystems?
● Percolation, porosity, fringe, recharge, and relation to
permeability surface water.
● Runoff
● Types of pollution that Describe how water is held in
affect groundwater soil
● Saltwater intrusion and and rock.
the water table
3 Lakes and Ponds Model the temperature How do humans impact
● Stratification stratification and turnover of eutrophication?
● Eutrophication lakes and ponds.
● Human impact on Why is pH important to
eutrophication organisms in an aquatic
ecosystem?
10 Flowing Water Identify and determine from How is a topographical map
● Major county stream and topographic maps the useful in predicting possible
tributaries following fundamentals of sources of pollution in a
● Stream structure stream structure, and relate watershed?
● Importance of water from this structure to the problems
streams of stream pollution. How does stream pollution
● Physical factors of affect wildlife habitats?
streams Distinguish between various
● Stream analysis physical factors on a freshwater Why are stream assessments
● Stream communities stream useful?
Calculating biotic index
and stream health Analyze a stream and How do we test for water
● Forest buffer determine the concentrations quality?
of various chemicals
What does the biotic index
Calculate the biotic index of tell us about the health of a
the stream and explain its stream?
connection to stream health.
How can forested buffer
Describe how a forested buffer zones improve stream
zone improves stream health. health?
9-10 Chesapeake Bay and Wetlands Identify the characteristics of What are the characteristics
● Characteristics of an an estuary. of estuaries?
estuary
● Geologic history of the Describe the geological history How do humans impact the
Chesapeake Bay of the Chesapeake Bay. Chesapeake Bay?
● Abiotic factors and
communities Compare and contrast drainage Why are wetlands
● Interdependent basins in the mountainous important?
relationships in the region, the Piedmont plateau
Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic coastal plain.
● Underwater grass
communities
● Impact of human
population over 200
years
● Wetland conservation
and development
decisions
● Habitat destruction
● Economic resources
● Population dynamics
● Native species
management
● Invasive species
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.