174x Filetype PDF File size 0.20 MB Source: www.bvmengineering.ac.in
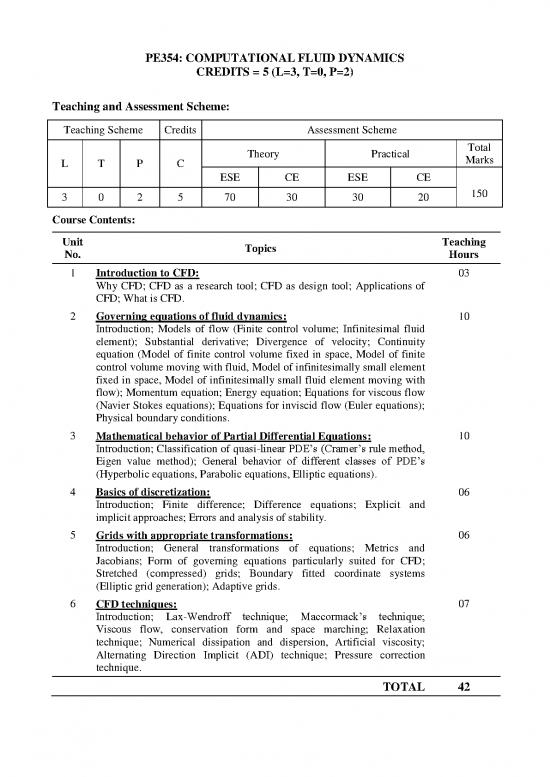
PE354: COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS
CREDITS = 5 (L=3, T=0, P=2)
Teaching and Assessment Scheme:
Teaching Scheme Credits Assessment Scheme
Theory Practical Total
L T P C Marks
ESE CE ESE CE
3 0 2 5 70 30 30 20 150
Course Contents:
Unit Topics Teaching
No. Hours
1 Introduction to CFD: 03
Why CFD; CFD as a research tool; CFD as design tool; Applications of
CFD; What is CFD.
2 Governing equations of fluid dynamics: 10
Introduction; Models of flow (Finite control volume; Infinitesimal fluid
element); Substantial derivative; Divergence of velocity; Continuity
equation (Model of finite control volume fixed in space, Model of finite
control volume moving with fluid, Model of infinitesimally small element
fixed in space, Model of infinitesimally small fluid element moving with
flow); Momentum equation; Energy equation; Equations for viscous flow
(Navier Stokes equations); Equations for inviscid flow (Euler equations);
Physical boundary conditions.
3 Mathematical behavior of Partial Differential Equations: 10
Introduction; Classification of quasi-linear PDE’s (Cramer’s rule method,
Eigen value method); General behavior of different classes of PDE’s
(Hyperbolic equations, Parabolic equations, Elliptic equations).
4 Basics of discretization: 06
Introduction; Finite difference; Difference equations; Explicit and
implicit approaches; Errors and analysis of stability.
5 Grids with appropriate transformations: 06
Introduction; General transformations of equations; Metrics and
Jacobians; Form of governing equations particularly suited for CFD;
Stretched (compressed) grids; Boundary fitted coordinate systems
(Elliptic grid generation); Adaptive grids.
6 CFD techniques: 07
Introduction; Lax-Wendroff technique; Maccormack’s technique;
Viscous flow, conservation form and space marching; Relaxation
technique; Numerical dissipation and dispersion, Artificial viscosity;
Alternating Direction Implicit (ADI) technique; Pressure correction
technique.
TOTAL 42
List of References:
1. J. D. Anderson, Jr., “Computational Fluid Dynamics: The basics with applications”,
International edition, Mc-Graw Hill, 1995.
2. Veersteeg and Malalasekara, “CFD: The finite volume method”, Prentice Hall, 1996.
3. A. W. Date, “Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics”, Cambridge University Press,
2005.
4. Goshdastidar, “Computer simulation of flow and heat transfer”, Tata Mc-graw Hill.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.