218x Filetype PDF File size 0.03 MB Source: vmrfdu.edu.in
PHARMACY PRACTICE
M. Pharm
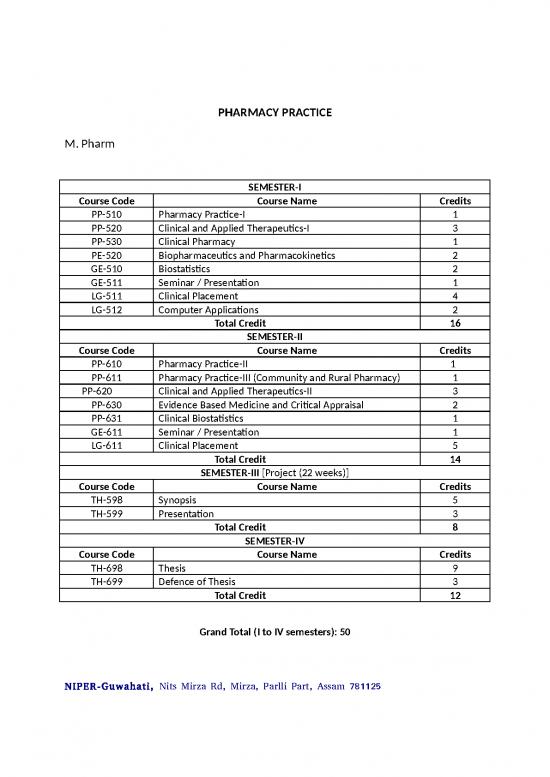
SEMESTER-I
Course Code Course Name Credits
PP-510 Pharmacy Practice-I 1
PP-520 Clinical and Applied Therapeutics-I 3
PP-530 Clinical Pharmacy 1
PE-520 Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics 2
GE-510 Biostatistics 2
GE-511 Seminar / Presentation 1
LG-511 Clinical Placement 4
LG-512 Computer Applications 2
Total Credit 16
SEMESTER-II
Course Code Course Name Credits
PP-610 Pharmacy Practice-II 1
PP-611 Pharmacy Practice-III (Community and Rural Pharmacy) 1
PP-620 Clinical and Applied Therapeutics-II 3
PP-630 Evidence Based Medicine and Critical Appraisal 2
PP-631 Clinical Biostatistics 1
GE-611 Seminar / Presentation 1
LG-611 Clinical Placement 5
Total Credit 14
SEMESTER-III [Project (22 weeks)]
Course Code Course Name Credits
TH-598 Synopsis 5
TH-599 Presentation 3
Total Credit 8
SEMESTER-IV
Course Code Course Name Credits
TH-698 Thesis 9
TH-699 Defence of Thesis 3
Total Credit 12
Grand Total (I to IV semesters): 50
NIPER-Guwahati, Nits Mirza Rd, Mirza, Parlli Part, Assam 781125
Pharmacy Practice
SEMESTER-I
PP-510
Pharmacy Practice-I (1 credit)
1. Understanding terminologies and concepts: Primary, secondary and tertiary care;
Pharmacy Practice; Institutional, hospital, ward clinical and community pharmacy; Patient
confidentiality, patient compliance, counseling, informed consent.
2. Pharmaceutical care and planning
3. Hospital pharmacy: Overview of organization and structure (comparison with community
pharmacy), basic hospital pharmacy services.
4. Specialized services e.g. Drug Information Centre and service provision.
5. Role of patients in decision-making regarding therapeutic management: Factors
affecting patients’ decision to take/not to take the medication.
6. Professional Responsibilities: Profession of pharmacy and pharmacists as practitioners;
Responsibilities of pharmacy practitioners as stated in developed countries; Relevance
and scope of adopting these in India; Opportunities and legislation; Relationship with
other health care professionals-doctors, nurses, paramedical staff, drug inspectors, excise
officers and police officers; Ethics of practice.
7. Skills: Communication, counseling; Reading, writing, thinking; Factors affecting
development of these skills.
Recommended books:
1. A Practical Guide to Contemporary Pharmacy Practice by Judith E. Thomson, Lippincott Williams
& Wilkins
2. Introduction to Hospital and Health-System Pharmacy Practice by David A. Holdford and Thomas
R. Brown
3. Communication Skills in Pharmacy Practice : A Practical Guide for Students and Practitioners, by
Robert S. Beardsley, Carole Kimberlin and William N. Tindall
4. Hospital Pharmacy by Martin Stephens
5. Hospital Pharmacy, by Willium Hassan, Lea &Febiger
NIPER-Guwahati, Nits Mirza Rd, Mirza, Parlli Part, Assam 781125
PP-520
Clinical and Applied Therapeutics-I (3 credits)
1. Geriatrics: Issues based on age related physiologic and pharmacokinetic/dynamic
changes; Variations in management from other patient groups; Pharmaceutical care
plan in view of compliance, ability to use devices for other diseases/disorders) including
discharge and home care plan.
2. Paediatrics: Specific childhood diseases and management; Immunizations, national
immunization programmes and scope for pharmacists’ involvement in these; Special
issues of paediatric management; Dosage adjustments based on age and physiological
and pharmacokinetic/dynamic development stage; Availability of ‘adequate’
formulations, dosage forms; Drug administration, timing: Compliance, psychology and
hormonal changes in adolescents.
3. Cardiology: Hypertension; Congestive heart failure
4. Cardiology: Angina; Myocardial Infection; Arrhythmias; Lipid disorders; Guidelines for
management of patient and monitoring drug therapy, TDM for digoxin.
5. Respiratory diseases and treatment: Asthma; COPD; TDM of Theophyllin; Use and
maintenance of different inhalers and devices, operation of oxygen cylinders; Monitoring
therapy; Guidelines ; Respiratory infections (treatment in view of resistant states,
isolation, monitoring therapy and duration of treatment , side effects, drug
interactions)-URTIs and LRTIs; TB, pneumonia.
6. Nephrology: Influence and important of fluid and electrolyte balance and acid-base
balance; Acute renal failure; Chronic renal failure; Renal dialysis (types and points of
pharmacists’ involvement).
7. Infections and antimicrobial therapy: Special emphasis on communicable diseases in
India, introduction to related national health programmes; UTIs, GI, CNS, bone and joint
infections, sexually transmitted diseases, mycotic parasitic infections; Need and
relevance of antibiotic polices.
8. Diabetes: Type 1 and 2 (incidence, prevalence, etiology, influencing factors, genetic
basis); Treatment option and guidelines; Insulin types and formulations, administration
monitoring therapy, patient education; Resistant cases (causes, alternatives to
treatment); Management of gestational diabetes.
Note: Applicable to all practice based subjects/topics
a) Teaching of individual drugs should not be included: Only specific practical as against
theoretical issues of drugs commonly used in practice should be discussed along with
the recent advances in drugs, formulations and dosage forms.
NIPER-Guwahati, Nits Mirza Rd, Mirza, Parlli Part, Assam 781125
b) Teaching should be practice and primary literature based with emphasis on issues in
therapy, advances and guidelines with case studies throughout the course.
c) In all areas, primary literature review and individual appraisal (as can be assessed in
practice) of recent developments is encouraged.
Recommended books:
1. Koda-Kimble and Young’s Applied Therapeutics: The Clinical use of Drugs by Brian K. Alldredge,
Robin L. Corelli, Michael E. Ernst, and B. Joseph Guglielmo
2. Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach by Joseph DiPiro, Robert L. Talbert, Gary Yee
and Gary Matzke
3. Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics by Eric T. Herfindal and Joseph L. Hirschman Clinical
Pharmacy and Therapeutics, by Robert Walker and Cate Whittlesea
4. Goodman and Gillman’s Manual of Pharmacology and Therapeutics by Laurence Brunton,
Donald Blumenthal, lain Buxton and Keith Parker
5. Goodman and Gillman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, by Laurence Brunton, Bruce
Chabner and Bjorn Knollman
PP-530
Clinical Pharmacy (1 credit)
1. Evolution of Clinical Pharmacy and current scenario (ward and clinical pharmacy services
responding to symptoms)
2. Modified release doses forms: Advantagesand limitations of modified release dosage
forms for patient treatment.
3. Update on advances in biotechnology and gene therapy
4. Biochemical and other laboratory data interpretation (in association with clinical
information and limitations of laboratory results): Case studies (Workshops) of renal,
hepatic, cardiac, respiratory, diabetic (including dose adjustment of insulin with glucose
monitoring), epileptic (including DIs, TDM) and elderly osteoporotic patients; Inclusion
of issues around hypo/hyperthyroid/thyrotoxicosis and anticoagulation therapy within
these cases.
5. Therapeutic drug monitoring of digoxin, theophylline, phenytoin phenobarbitone,
carbamazepine and gentamicin
6. Understanding audit: Auditcycle, identifyingkey issues, setting standards; Audit process;
Results and re-audit
7. Clinical trials and pharmacists’ involvement: Legal and ethical requirements of trials
8. Research Methods: Designing, planning and carrying out a research project; Research
methodologies (quantitative, qualitative) – uses, adequacy and limitations; Choice of
NIPER-Guwahati, Nits Mirza Rd, Mirza, Parlli Part, Assam 781125
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.