148x Filetype PDF File size 0.21 MB Source: phoenix.ieu.edu.tr
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
Study Questions for ECON 101 Midterm Exam II-(Fall 2015/2016)
Multiple Choice Questions
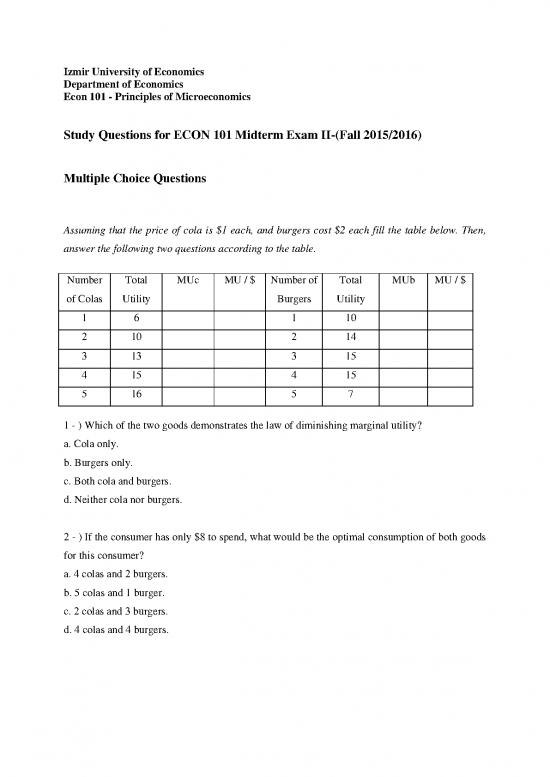
Assuming that the price of cola is $1 each, and burgers cost $2 each fill the table below. Then,
answer the following two questions according to the table.
Number Total MUc MU / $ Number of Total MUb MU / $
of Colas Utility Burgers Utility
1 6 1 10
2 10 2 14
3 13 3 15
4 15 4 15
5 16 5 7
1 - ) Which of the two goods demonstrates the law of diminishing marginal utility?
a. Cola only.
b. Burgers only.
c. Both cola and burgers.
d. Neither cola nor burgers.
2 - ) If the consumer has only $8 to spend, what would be the optimal consumption of both goods
for this consumer?
a. 4 colas and 2 burgers.
b. 5 colas and 1 burger.
c. 2 colas and 3 burgers.
d. 4 colas and 4 burgers.
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
3 - ) If MUa / Pa=1.5 and MUb / Pb=3 for a consumer who is spending her entire budget, then to
maximize utility she should
a. buy more of product A and less of product B.
b. buy more of product B and less of product A.
c. not change her situation.
d. None of the above.
4 - ) A fall in the price of Pepsi that causes a household to shift its purchasing pattern away from
substitutes and toward Pepsi is the
a. income effect of a price change.
b. substitution effect of a price change.
c. complementary effect of a price change.
d. diminishing marginal utility effect of a price change.
5 - ) Assume leisure is a normal good. The substitution effect of a wage decrease implies a
__________ demand for leisure and a __________ labor supply.
a. lower; higher
b. higher; lower
c. higher; higher
d. lower; lower
6 - ) Economic costs
a. include both a normal rate of return on investment and the opportunity cost of each factor of
production.
b. are equal to the direct costs of hiring all factors of production.
c. are the opportunity cost of each factor of production minus any interest charges paid on
borrowed funds.
d. are equal to total revenue minus accounting profit.
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
7 - ) The explanation for why marginal cost is positive and rising in the short run is _______
marginal product of labor in the production process.
a. a zero
b. a constant
c. an increasing
d. a diminishing
8- ) The information a firm needs to know with the objective of maximizing profit includes:
a. The market price of the output
b. The techniques of production that are available
c. The prices of inputs
d. All of the above
9 - ) Firms that are earning zero economic profits are
a. breaking even
b. shutting down in the long run
c. earning less than a normal rate of return
d. shutting down in the short run
10 - ) In the long run, a firm
a. can vary all inputs, but it cannot change the mix of inputs it uses
b. has no fixed factors of production
c. can shut down, but it cannot exit the industry
d. must make positive economic profits
11 - )If marginal product is greater than average product, then
a. average product must be decreasing.
b. marginal product must be decreasing.
c. marginal product must be increasing.
d. marginal product could either be increasing or decreasing.
Izmir University of Economics
Department of Economics
Econ 101 - Principles of Microeconomics
Table 1
Inputs Required to Produce a Product Using Alternative Technologies
12 - ) Refer to Table 1. Which technology is the most capital intensive?
a. A b. B c. C d. D
13- ) Refer to Table 1. If the hourly wage rate is $10 and the hourly price of capital is $50, which
production technology should be selected?
a. A b. B c. C d. D
14 - ) A factory produces 1,000 radios a year. Average variable cost (AVC) is $10 and total fixed
cost is $5,000. Thus, the factory’s total cost (TC)
a. Equals $5,010.
b. Equals $6000
c. Equals $15000
d. Equals $5,000,000
15 - ) A characteristic of perfect competition is that
a. It is difficult for new firms to enter the industry
b. The firm can influence the product’s price
c. The firms in the industry produce a homogenous product
d. The firm produces a large share of the industry’s total product
16 - ) In perfect competition, the marginal revenue curve
a. and the demand curve facing the firm are identical.
b. is always above the demand curve facing the firm.
c. is always below the demand curve facing the firm.
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.