235x Filetype PDF File size 0.30 MB Source: fluencyfast.com
Arabic Curriculum
ARABIC ALPHABET
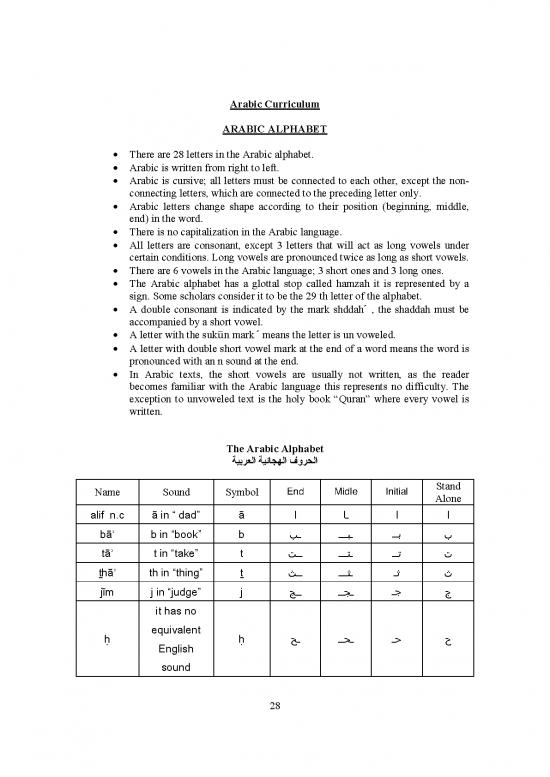
• There are 28 letters in the Arabic alphabet.
• Arabic is written from right to left.
• Arabic is cursive; all letters must be connected to each other, except the non-
connecting letters, which are connected to the preceding letter only.
• Arabic letters change shape according to their position (beginning, middle,
end) in the word.
• There is no capitalization in the Arabic language.
• All letters are consonant, except 3 letters that will act as long vowels under
certain conditions. Long vowels are pronounced twice as long as short vowels.
• There are 6 vowels in the Arabic language; 3 short ones and 3 long ones.
• The Arabic alphabet has a glottal stop called hamzah it is represented by a
sign. Some scholars consider it to be the 29 th letter of the alphabet.
• A double consonant is indicated by the mark shddahّ , the shaddah must be
accompanied by a short vowel.
• A letter with the sukūn mark ْ means the letter is un voweled.
• A letter with double short vowel mark at the end of a word means the word is
pronounced with an n sound at the end.
• In Arabic texts, the short vowels are usually not written, as the reader
becomes familiar with the Arabic language this represents no difficulty. The
exception to unvoweled text is the holy book “Quran” where every vowel is
written.
The Arabic Alphabet
ﺔﻴﺑﺮﻌﻟا ﺔﻴﺋﺎﺠﻬﻟا فوﺮﺤﻟا
End Midle Initial Stand
Name Sound Symbol Alone
alif n.c ā in “ dad” ā ا ﺎـ ا ا
bāʾ b in “book” b ﺐـ ـــﺒـ ــﺑ ب
tāʾ t in “take” t ﺖــ ـــﺘـ ــﺗ ت
ṯhāʾ th in “thing” ṯ ﺚــ ـــﺜـ ـﺛ ث
jīm j in “judge” j ﺞــ ــﺠـ ـﺟ ج
it has no
ḥ equivalent ḥ ﺢـ ــﺤـ ـﺣ ح
English
sound
28
it has no
ḫāʾ equivalent ḫ ﺦـ ــﺨـ ـﺧ خ
English
sound
dāl n.c d in “dad” D ﺪﺪــ دــ د
ḏāl n.c th in “that” ḏ ﺬﺬــ ذــ ذ
raʾ n.c r in “row” R ﺮﺮـ رـ ر
zāy n.c z in “zebra” Z ﺰﺰـ زـ ز
sīn s in “sack” S ـﺲـ ـﺴـ سﺳ
shīn sh in “shot” sh ـﺶـ ـﺸـ شﺷ
it has no
ṣād equivalent ṣ ـﺺـ ـﺼـ صﺻ
English
sound
it has no
ḍāḍ equivalent ḍ ـﺾـ ـﻀـ ضﺿ
English
sound
it has no
ṭāʾ equivalent ṭ ـﻂـ ـﻄـ طﻃ
English
sound
it has no
ẓāʾ equivalent ẓ ـﻆـ ـﻈـ ظﻇ
English
sound
it has no
aʿyn equivalent ʿ ﻊـ ـﻌـ ـﻋ ع
English
sound
29
it has no
ġayn equivalent ġ ـﻎـ ـﻐـ غﻏ
English
sound
fāʾ f in “fat” f ـﻒـ ـﻔـ فﻓ
it has no
qāf equivalent q ـﻖـ ـﻘـ قﻗ
English
sound
kāf k in “black” k ـﻚـ ـﻜـ كﻛ
lām l in “leg” l ـﻞـ ـﻠـ لﻟ
mīm m in “man” m ـﻢـ ـﻤـ مﻣ
nūn n in “noon” n ـﻦـ ـﻨـ نﻧ
hāʾ h in “hat” h ـﻪـ ـﻤـ ـﻣ ﻫ
wāw n.c w in “war” w ﻮﻮـ وـ و
yāʾ y in “yet” y ـﻲـ ـﻴـ ىﻳ
hamzah ʾ ء * أ ء
n.c : non-connecting letters.
* can take different form depending on vowels أ ـــﺋ ؤ
30
Vowels
Short Vowels Long Vowels Tanween
letter/lesymbo َ◌ ا ً◌
name fatiḥa alif tanween
sound a as “hat” ā as “dad” an
letter/symbole ِ◌ ـﻳ ٍ◌
name kasrah yāʾ tanween
sound i as “sit” ī “seed” in
letter/symbole ُ◌ و ٌ◌
name dammah waw tanween
sound u “put” ū “shoot” un
The alif works as a long vowel when preceded by a letter with a fatiḥa.
The yāʾ works as a long vowel when preceded by a letter with a kasrah.
The waw works as a long vowel when preceded by a letter with a dammah.
There are three additional marks that helps with the correct pronunciation of
Arabic words:
First is madda آ and it is written on top of the alif to indicate a longer sound,
instead of writing 2 alifs (ا ا).
Second is sukun ْ , to indicate that the letter has no vowels, so to emphasis the
letter we make a brief pause.
Third is the shddah ّ ,and it is used to give a double sound to the letter. For
example wasal and wssal ﻞَّﺻو و ﻞﺻو
31
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.