242x Filetype PDF File size 0.24 MB Source: www.costellomedical.com
The Prevalence and Characteristics of Lay Summaries of 5
Published Journal Articles
Maria Haughton and Danielle Machin
Costello Medical Consulting Ltd, Cambridge, UK
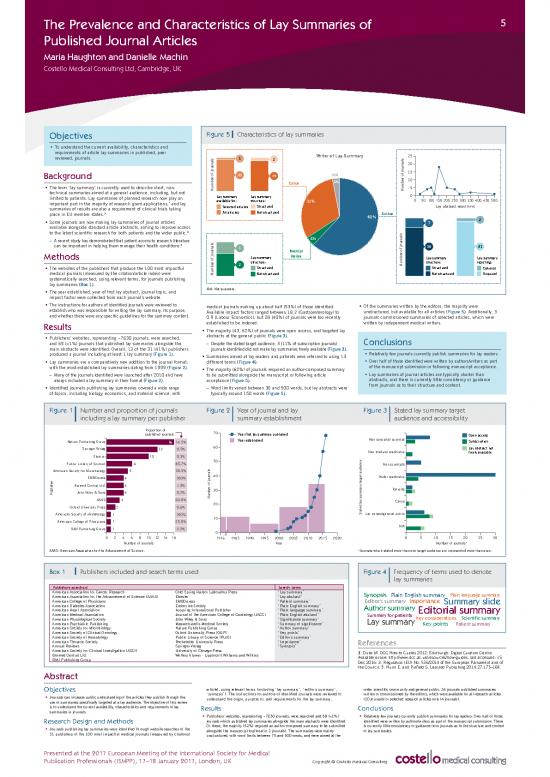
Objectives Figure 5 Characteristics of lay summaries
To understand the current availability, characteristics and
requirements of article lay summaries in published, peer Writer of Lay Summary
reviewed, journals. 1 2 25
20
20 N/A 15
Background 19
Editor 3% 10
The term ‘lay summary’ is currently used to describe short, non- Number of journals Number of journals5
technical summaries aimed at a general audience, including, but not 0
limited to patients. Lay summaries of planned research now play an Lay summary Lay summary
1 available for: structure: 31% 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
important part in the majority of research grant applications, and lay Selected articles Structured Lay abstract word limit
summaries of results are also a requirement of clinical trials taking All articles
place in EU member states.2 Not structured Author
62% 2
Some journals are now making lay summaries of journal articles 7
available alongside standard article abstracts, aiming to improve access
3
to the latest scientific research for both patients and the wider public.
– A recent study has demonstrated that patient access to research literature 4%
3
can be important in helping them manage their health conditions. 1 36 41
Medical
Methods Lay summary Writer Lay summary Lay summary
2 structure: Number of journalsstructure: reporting:
The websites of the publishers that produce the 100 most impactful Structured Structured Optional
medical journals (measured by the citation/article index) were Number of journals Not structured Not structured Required
systematically searched, using relevant terms, for journals publishing
lay summaries (Box 1).
The year established, year of first lay abstract, journal topic, and N/A: Not available.
impact factor were collected from each journal’s website.
The instructions for authors of identified journals were reviewed to medical journals making up about half (53%) of those identified. Of the summaries written by the editors, the majority were
establish who was responsible for writing the lay summary, its purpose, Available impact factors ranged between 18.2 (Gastroenterology) to unstructured, but available for all articles (Figure 5). Additionally, 3
and whether there were any specific guidelines for the summary content. 0.9 (Labour Economics), but 28 (40%) of journals were too recently journals commissioned summaries of selected articles, which were
Results established to be indexed. written by independent medical writers.
The majority (43, 62%) of journals were open access, and targeted lay
Publishers’ websites, representing ~7630 journals, were searched, abstracts at the general public (Figure 3).
and 69 (<1%) journals that published lay summaries alongside the – Despite the stated target audience, 3 (11% of subscription journals) Conclusions
main abstracts were identified. Overall, 13 of the 31 (41%) publishers journals identified did not make lay summaries freely available (Figure 3).
produced a journal including at least 1 lay summary (Figure 1). Summaries aimed at lay readers and patients were referred to using 13 Relatively few journals currently publish summaries for lay readers.
Lay summaries are a comparatively new addition to the journal format, different terms (Figure 4). Over half of those identified were written by authors/writers as part
with the most established lay summaries dating from 1999 (Figure 2). The majority (62%) of journals required an author-composed summary of the manuscript submission or following manuscript acceptance.
– Many of the journals identified were launched after 2010 and have to be submitted alongside the manuscript or following article Lay summaries of journal articles are typically shorter than
always included a lay summary in their format (Figure 2). acceptance (Figure 5). abstracts, and there is currently little consistency or guidance
Identified journals publishing lay summaries covered a wide range – Word limits varied between 30 and 500 words, but lay abstracts were from journals as to their structure and content.
of topics, including biology, economics, and material science, with typically around 150 words (Figure 5).
Figure 1 Number and proportion of journals Figure 2 Year of journal and lay Figure 3 Stated lay summary target
including a lay summary per publisher summary establishment audience and accessibility
Proportion of 70
published journals Year first lay summary published Open access
Nature Publishing Group 16 14.5% Year established Non-specialist scientist Subscription
Springer-Verlag 12 0.5% 60 Lay abstract not
Non-medical readership freely available
Elsevier 10 0.3%
Public Library of Science 6 85.7% 50 Non-scientists
American Society for Microbiology 5 38.5%
EMBOpress 4 100% 40 Wider readership
Biomed Central Ltd. 4 1.5%
30 Patients
Publisher John Wiley & Sons 4 0.2%
AAAS 3 60.0% Number of journals
20 Carers
Oxford University Press 2 0.6%
American Society of Hematology 1 100% Stated lay summary target audienceLay person/general public
American College of Physicians 10
1 25.0%
BMJ Publishing Group 1 2.2% N/A
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 1916 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 0 5 10 15 20 25 30
Number of journals Year Number of journals*
AAAS: American Association for the Advancement of Science. *Journals which stated more than one target audience are represented more than once.
Box 1 Publishers included and search terms used Figure 4 Frequency of terms used to denote
lay summaries
Publishers searched Search terms
American Association for Cancer Research Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press “Lay summary” Synopsis Plain English summary Plain language summary
American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) Elsevier “Lay abstract”
American College of Physicians EMBOpress “Patient summary” Editor’s summary Importance Summary slide
American Diabetes Association Endocrine Society “Plain English summary” Author summary
American Heart Association Ivyspring International Publisher “Plain language summary” Editorial summary
American Medical Association Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) “Plain English abstract” Summary for patients Key considerations Scientific summary
American Physiological Society John Wiley & Sons “Significance summary” Lay summary
American Psychiatric Publishing Massachusetts Medical Society “Summary of significance” Key points Patient summary
American Society for Microbiology Nature Publishing Group “Author summary”
American Society of Clinical Oncology Oxford University Press (OUP) “Key points”
American Society of Hematology Public Library of Science (PLoS) “Editor’s summary”
American Thoracic Society Rockefeller University Press “Importance” References
Annual Reviews Springer-Verlag “Synopsis”
American Society for Clinical Investigation (ASCI) University of Chicago Press 1. Duke M. DCC How-to Guides 2012; Edinburgh: Digital Curation Centre.
Biomed Central Ltd. Wolters Kluwer - Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Available online: http://www.dcc.ac.uk/resources/how-guides, last accessed: 15
BMJ Publishing Group Dec 2016; 2. Regulation (EU) No. 536/2014 of the European Parliament and of
the Council; 3. Nunn E. and Pinfield S. Learned Publishing 2014;27:173–184.
Abstract
Objectives article), using relevant terms (including “lay summary”, “editor’s summary”, wider scientific community and general public. 24 journals published summaries
Journals can increase public understanding of the articles they publish through the “synopsis”). The instructions for authors of identified journals were reviewed to written or commissioned by the editors, which were available for all research articles
use of summaries specifically targeted at a lay audience. The objective of this review understand the origin, purpose of, and requirements for the lay summary. (20 journals) or selected research articles only (4 journals).
is to understand the current availability, characteristics and requirements of lay Results Conclusions
summaries in journals.
Publishers’ websites, representing ~7630 journals, were searched and 69 (<1%) Relatively few journals currently publish summaries for lay readers. Over half of those
Research Design and Methods journals which published lay summaries alongside the main abstracts were identified. identified were written by authors/writers as part of the manuscript submission. There
Journals publishing lay summaries were identified through website searches of the Of these, the majority (62%) required an author-composed summary to be submitted is currently little consistency or guidance from journals as to the structure and content
31 publishers of the 100 most impactful medical journals (measured by citations/ alongside the manuscript (optional in 2 journals). The summaries were mainly of lay summaries.
unstructured, with word limits between 75 and 500 words, and were aimed at the
Presented at the 2017 European Meeting of the International Society for Medical
Publication Professionals (ISMPP), 17–18 January 2017, London, UK Copyright © Costello Medical Consulting
no reviews yet
Please Login to review.